These posters have been presented at meetings in Children's Mercy and around the world. They represent research that was done at the time they were created, and may not represent medical knowledge or practice as it exists at the time viewers access these posters.
-

A novel way to describe variation in antibiotic use
Adrienne G. DePorre, Troy Richardson, Jason Newland, and Mark Neuman
Background: A broader understanding of antibiotic variation can inform stewardship efforts. Diversity indices are frequently calculated in ecologic studies to measure the variety of species in a given habitat, however they have not yet been used to study variation in antibiotic use in the healthcare setting.
Objective: To develop a novel assessment of antibiotic variation, based on the breadth of an antibiotic’s associated conditions as well as its use, measured by days of therapy (DOT).
Design/Methods: We assessed antibiotic use in children aged 60 days-18 years hospitalized at a US Children’s hospital included in the Pediatric Health Information System (PHIS) database. We identified common antibiotics, defined as those that account for >1% of total antibiotic DOT at >80% of hospitals. An antibiotic diversity index (ADI) was calculated for each antibiotic at each hospital using the number of conditions and DOT to mimic the Shannon-Weiner entropy index, an index used in ecology to measure the complexity of an ecosystem. Hospital-level variation in antibiotic use was measured by the spread of ADI scores across hospitals relative to the mean ADI (i.e. coefficient of variation [CV]).
Results: Table 1 shows commonly used antibiotics at 49 hospitals. Cefazolin has the highest mean ADI indicating it is used in the highest number of conditions. However, it also has the smallest CV indicating consistent use across hospitals. . Conversely, meropenem has a relatively small mean ADI but has the highest CV. This indicates that meropenem is used in a relatively small number of conditions but is used more variably across hospitals. Figure 1 shows the utility of the ADI to identify variation in distribution of both an antibiotic’s DOT and associated conditions. In most hospitals, use of cefazolin is focused consistently in 7-9 conditions while meropenem is used consistently across hospitals in 2-3 conditions.
Conclusion(s): ADI is a novel tool to measure variability in antibiotic use across hospitals. Comparisons of ADIs highlight antibiotics associated with unequal patterns of use and their associated conditions.Presented at the 2021 PAS Virtual Conference
-

Antibiotic Durations for Skin and Soft Tissue Infections in Pediatric Urgent Care Clinics
Megan Hamner, Amanda Nedved, Holly Austin, Donna Wyly, Alaina N. Burns, Diana King, Brian R. Lee, and Rana El Feghaly
Background: Skin and soft tissue infections (SSTIs) are the second most common diagnosis leading to pediatric antibiotic prescriptions in the outpatient setting after respiratory diagnoses. However, most antibiotic stewardship programs have mainly focused on the latter. Children seen in the ambulatory setting for SSTIs often receive >7 days of antibiotics, although current society guidelines recommend 5-7 days for most diagnoses.
Objective: To determine the baseline percentage of patients receiving antibiotic prescriptions for >7 days for SSTIs in urgent care clinics (UCC)s of a pediatric health system and to evaluate factors that influence providers towards longer durations.
Design/Methods: We built a report that extracted patient encounters from the three UCCs based on International Classification of Diseases (ICD)-10 codes for common SSTIs including impetigo, abscesses, cellulitis, erysipelas, folliculitis, paronychia, and animal bites. Data was pulled from June 2019 through June 2020. The report included patient age, concomitant diagnoses, antibiotics prescribed and their duration. We excluded encounters if the patient was transferred to the emergency department or admitted, the patient was younger than 3 months of age, no antibiotics were prescribed, or if there was a concurrent infectious diagnosis affecting antibiotic duration. We sent a 22-question survey to UCC providers to understand prescribing habits particularly focusing on factors prompting administration of longer antibiotic courses.
Results: From June 2019-June 2020, we reviewed 2,575 encounters; we excluded 208 of those (8%). 823 (35%) of patients received >7 days of antibiotics for SSTIs while 1181 (50%) received 5-7 days and 35 (1%) received <5 days of antibiotics. 328>(14%) received topical therapy only. Most common antibiotics prescribed included cephalexin, clindamycin, and trimethoprim-sulfamethoxazole. A mild improvement in the 5-7 days duration was noted through our study period (Figure 1). The survey was sent to 50 providers with 27 responding (54% response rate) (Tables 1 and 2). Barriers for shorter treatment courses included concern for acute rheumatic fever development, parental pressure, fear of complications, and accustomed antibiotic duration.
Conclusion(s): A third of children with SSTIs in our UCCs receive long courses of antibiotics. A mild improvement noted in our study period may be due to existing antibiotic stewardship interventions. Specific provider concerns leading to overprescribing will be targeted by quality improvement efforts.Presented at the 2021 PAS Virtual Conference
-

A SMARTer Way to Round
Charles Maloy, Adrienne G. DePorre, Erica Adams, Jessica Olson, Amber Hunley, and Darcy K. Weidemann
Background: Communication is a key driver of health care outcomes. Poor communication practices contribute to sentinel safety events, poor family/patient experiences, and delays in care. Use of checklists in the healthcare setting is important to the development of high reliability and is increasingly common, however, the development and implementation of medical checklists for the standard patient floor are inadequately described.
Objective: To develop a sustainable rounding checklist for multidisciplinary discussion of patient safety measures and clinical plans.
Design/Methods: Key stakeholders in the rounding process (subspecialty and general pediatrics physicians, resident physician, bedside nurses, and nursing leadership) created a rounding checklist tool for use on a medical unit at our tertiary care children’s hospital. This checklist was modified from an existing checklist used in the pediatric intensive care unit. It focused on reducing harm, improving quality of care, and facilitating communication. To foster open communication within the multidisciplinary team and project sustainability, bedside nurses owned the task to prompt daily review of checklist items with the team during rounds. We developed badge buddies as an aid and an audit tool to assess checklist compliance. Compliance with checklist use was assessed by iterative Plan-Do-Study-Act (PDSA) cycles. Acceptability and usefulness of the checklist was measured by a 6 month-post implementation survey of nurses, residents, and staff.
Results: A five-item checklist entitled SMART (Situational Awareness, Medications, Access, Routine, and Transition) was created (Figure 1). Daily audits showed between 75%-88% usage of the checklist during rounds (Figure 2). Our first PDSA cycle showed improved compliance with implementation of a streamlined audit tool. 29% of eligible providers completed the survey (n=51). 77% of respondents perceived communication improvement with SMART card usage with 4% disagreement. 66% reported vital patient care details were discussed that would otherwise have been missed. Only 2% found the checklist led to delays in patient care with a majority responding that checklist completion took 30-60 seconds.
Conclusion(s): This project emphasizes the importance of multidisciplinary teams in development and implementation of a daily rounding checklist for a pediatric floor. We demonstrate the feasibility and acceptability of inserting a rounding checklist into the workflow of a multidisciplinary pediatric care team. Further study is needed to determine long-term effects on this initiative on process of care outcomes.Presented at the 2021 PAS Virtual Conference
-

Assessing the Effects of Social Determinants on Serious Safety Events
Lisa L. Schroeder, Jessi Van Roekel, and John Cowden
Background: We have long known that various social determinants of health (SDH) such as race, gender, socioeconomic status and others can affect health outcomes, such as readmission rates and mortality. To our knowledge, the impact of SDH on safety events has not been studied.
Objective: We sought to understand the role that social determinants may play in contributing to safety events at our institution and to incorporate this information into the creation of corrective action items following the serious safety event.
Design/Methods: The Clinical Safety team partnered with the Office of Equity and Diversity to develop a standard question regarding the potential influence of any SDH to be asked of each staff member interviewed after a potential serious safety event. The question was asked at the end of the interview and was read to maintain consistency. The question was modified early in the process based on feedback from the interviewers and the staff interviewed. All identified factors were collected, and the clinical safety team ultimately determined the likelihood that factors contributed to the adverse outcomes.
Results: Over the first two and a half years, 129 interviews were conducted spanning 20 safety events. The question was asked in 101 (78%) of the interviews. It was asked more consistently as the project went on, with only 58% in interviewees being asked the first year and 90% thereafter. At least one social determinant was identified as potentially contributing to the safety event in 21 interviews (11 cases). In these cases, an average of 1.36 factors were identified (range 1-3). Language and socioeconomic status were the most frequently identified factors. Responses to the social determinants question were then considered throughout the Root Cause Analysis process, including the development of action items.
Conclusion(s): By treating health equity as fundamental to patient safety, we integrated a question on the potential impact of SDH on safety events. Socialization to the process took time, but staff have now expressed increased awareness of the potential effects of social determinants. The consideration of impact of SDH on adverse events has informed the improvement team in their development of action items. The success of this project has led to the incorporation of health equity questions into other areas, including Performance Improvement, Evidence Based Practice, Patient Family Experience, and others. We hope to incorporate a similar question into the overall event reporting system to help inform future initiatives.Presented at the 2021 PAS Virtual Conference
-

Association Between ESA Dose and Blood Pressure in Pediatric Patients on Dialysis
Heather A. Morgans, Judith Sebestyen VanSickle, Franz Schaefer, and Bradley A. Warady
Background: Hypertension is a reported side effect of Erythropoiesis Stimulating Agents (ESAs), with a mechanism of action related to elevated hematocrit levels and direct vasopressor effects. Limited information exists on the relationship between ESA dosage and hypertension in children receiving maintenance dialysis.
Objective: The primary aim of this study was to determine whether there is a significant correlation between ESA dose and blood pressure (BP) in pediatric patients on dialysis. The secondary aim was to determine confounding variables in relation to ESA dose and BP.
Design/Methods: Data from the International Pediatric Dialysis Network (IPDN) database was used to retrospectively evaluate the association between ESA dose and BP. Data collected from January 2007 to September 2019 was analyzed. Systolic and diastolic BP measurements obtained at clinic visits were averaged and standardized based on age, height, and sex. ESA dose was measured in units/kg/week with Darbepoetin and continuous erythropoietin receptor activator (CERA) converted to equivalent units of Epogen. The confounding variables analyzed include hemoglobin level, BMI, dialysis modality, total fluid output (daily ultrafiltrate plus 24-hour urine output), number of antihypertensive medications, and use of growth hormone. Linear regression with Pearson correlation was used to analyze continuous variables.
Results: A total of 3790 children were included in the analysis with a mean age of 11 years and 55.7% male. The mean prescribed dose of ESA was 192 units/kg/week. A significant positive correlation was noted between ESA dose and systolic BP (p < 0.001) although there was no significant correlation with diastolic BP (p=0.2). Further evaluation showed a significant negative correlation between ESA dose, total fluid output, and hemoglobin level in univariate and multivariate analysis, p < 0.001.
Conclusion(s): The preliminary results from this study suggest that there may be a correlation between higher doses of ESAs and higher systolic BP in children receiving maintenance dialysis. Ongoing analysis of confounding variables will be helpful in determining the full correlation between ESA dose and BP.Presented at the 2021 PAS Virtual Conference
-
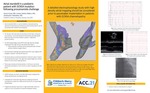
Atrial standstill in a pediatric patient with SCN5A mutation following procainamide challenge
Anmol Goyal, Lindsey Malloy-Walton, and Christopher Follansbee
Background: Atrial standstill (AS) is a rare arrhythmia characterized by absence of electrical and mechanical atrial activity associated with SCN5A channelopathy.
Case: An 18 year old male with structurally normal heart, frequent sinus pauses, nonsustained atrial tachycardia and high-grade block was found to have SCN5A mutation c.3823G>A (p.Asp1275Asn). An electrophysiology study (EPS) with high density voltage mapping of the right atrium was done (Fig 1a). Nonsustained multifocal atrial tachycardia was induced without ablative targets (Fib 1b). Procainamide challenge was negative for Brugada, however induced AS (Fig 1c-d). No atrial capture could be achieved at maximal output. Empiric atrial lead positioning in the right atrial appendage was utilized based on prior atrial mapping (Fig 1e). AS resolved in <24 hours with resultant functioning of the atrial>lead.
Decision-Making: SCN5A disease can have a variable phenotype ranging from asymptomatic to progressive AS. A detailed EP study with high density mapping should be considered to assess for viable atrial tissue prior to pacemaker implantation. Progressive disease may result in high thresholds, failure to capture or AS, and patients should be followed closely.
Conclusion: SCN5A channelopathy can result in a unique phenotype that requires careful and serial evaluation by an electrophysiologist. As progressive AS can occur, a detailed EPS with high density atrial mapping should be considered when pacemaker implantation is required.
-
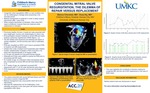
CONGENITAL MITRAL VALVE REGURGITATION, THE DILEMMA OF REPAIR VERSUS REPLACEMENT
Bianca Cherestal and Doaa Aly
Background: Congenital mitral regurgitation is a rare condition and can be challenging to manage when presenting in the neonatal period.
Case: Two week old male presented with poor weight gain, murmur and cardiomegaly on chest X-ray. Echocardiogram showed moderate to severe mitral regurgitation (MR) and suprasystemic pulmonary hypertension (PHN) (fig 1 a, b). The mitral valve (MV) leaflets were thickened and tethered with failure of central coaptation. PHN was classified as WHO I and II (due to persistent PHN of newborn and MR respectively). Inhaled nitric oxide, Enalapril and Furosemide were initiated. Cardiac catheterization revealed PVRi of 8.9 WU x m2 and CT was non-specific for lung parenchymal disease. Sildenafil and Flolan were added to reverse PHN prior to proceeding with MV repair. At 4 weeks of age he underwent mitral valvuloplasty which was complicated by severe MR and left heart failure (fig 1 c-d). Successful MV replacement with 17 mm St Jude mechanical valve was performed at 11 weeks (fig 1 e). PHN medications were weaned and patient is now ready for discharge.
Decision Making: Patient presented with severe left heart failure and PHN secondary to severe congenital MR. MV intervention was indicated due to failed medical management. While MV replacement, can be a challenge, it was ultimately necessary given the severe post repair residual regurgitation.
Conclusion: This case highlights the complexity of decision making for congenital MR, and the role of MV replacement in the case of failed repair.
-

Constrictive Pericarditis After Repair of a Ruptured Sinus of Valsalva
Sarah Studyvin and Sanket Shah
Background: Constrictive pericarditis (CP) is a rare complication of cardiac surgery. We report a patient who developed CP after ruptured sinus of Valsalva (RSOV) repair.
Case: A 23-year-old male presented with severe exertional dyspnea one year after RSOV repair. Echocardiogram showed thickened pericardium, ventricular septal bounce (Fig 1A), left atrial enlargement, diastolic hepatic flow reversal (Fig 1B), and trivial mitral regurgitation without stenosis. He underwent cardiac catheterization, which revealed elevated filling pressures (RVEDP 16 mmHg, LVEDP 18 mmHg), RVEDP/RVSP ratio < 0.5, and a low cardiac index (1.65 L/min/m2). Cardiac MRI on the same day confirmed pericardial thickening (Fig D) with paradoxic septal motion, dilated pulmonary veins (Fig 1F) and retrograde flow in the SVC.
Decision‐making: Pericardiectomy of thickened and adherent pericardium was performed without the use of cardiopulmonary bypass. The central venous pressure decreased from 23 to 7 mmHg and TEE showed normal systolic function with less septal bounce posteroperatively. Pathology specimens of the pericardium exhibited fibrosis and mild chronic inflammation. He continued to do well off diuretics at one-month follow-up.
Conclusion: Constrictive pericarditis is an uncommon complication of aortic root surgery. MRI is the ideal study to confirm the thickened pericardium and paradoxic septal motion in patients with suspected pericarditis. Cardiac catheterization can be performed to confirm the diagnosis.
-

C-reactive protein values to predict sepsis-induced inflammatory response in premature infants
Megan Tucker, Hung-Wen Yeh, Daniel K. Oh, and Venkatesh Sampath
Background: C-reactive protein (CRP) is an inflammatory marker that has been recognized as a biomarker of the systemic inflammatory response in preterm neonates. We hypothesized that initial and peak CRP values would correlate with the degree of sepsis-induced acute lung injury (ALI) as measured by the pulmonary severity score (PSS).
Objective: 1) Determine if confirmed (CF) sepsis events are associated with higher initial and peak CRP values than rule out (RO) sepsis events. 2) Investigate if initial and/or peak CRP correlates with severity of sepsis-induced ALI as measured by the PSS.
Design/Methods: In this retrospective case control study, we included infants < 31 weeks gestational age and < 1500 grams with late onset sepsis and RO sepsis events (blood culture negative, antibiotics continued 48-72 hours (hr)). We collected initial CRP values at the time of sepsis diagnosis and the peak CRP value recorded during the treatment period. Sepsis subtypes were defined as blood culture positive (Cx+), necrotizing enterocolitis (NEC), urinary tract infection (UTI), and culture negative (Cx-) sepsis (blood culture negative; antibiotics > 6 days). We collected the PSS, a validated score for lung injury, at different time points during the sepsis events starting at 72hr before and up to 168hr after sepsis diagnosis.
Results: We analyzed 211 CF and 123 RO sepsis events. Initial and peak CRP values were significantly higher in the CF sepsis group vs the RO sepsis group [median and interquartile range 1.8 (0.7, 4.5) vs. 0.6 (0.5-1.1), p <0.01 for initial values and 3.6 (0.8, 8.7) vs. 0.8 (0.5, 1.4), p < 0.01 for the peak values] (Figure 1). The changes from the initial CRP to the peak CRP were also greater in the CF sepsis events than in the RO events (F(1,335)=8.41, p value 0.004) (Figure 2). The relationship between PSS and CRP varied over time becoming more significant after sepsis diagnosis (F(7,1245)=2.77, p=0.0074) (Figure 3). Lastly, the changes from the initial to the peak CRP levels were different across sepsis subtypes with larger changes observed in the Cx+ and NEC groups than in UTI, Cx-, and RO sepsis (F(4,377)=2.92, p=0.02, Figure 4).
Conclusion(s): These results indicate that CRP is significantly higher both initially and at peak values in infants with CF vs RO sepsis events. Furthermore, CRP values correlate with PSS over time suggesting that CRP is not only a marker for sepsis/systemic inflammatory response but can potentially predict the severity of sepsis-induced ALI.Presented at the 2021 PAS Virtual Conference
-

Developing a Breastfeeding Advocacy Agenda through Insight from Breastfeeding Experiences of Faculty Physicians
Pooja French, Elizabeth Simpson, Courtney Winterer, Jodi Dickmeyer, and Sarah Stone
Background: Despite forward progress in recent decades surrounding lactation support, physician mothers continue to face challenges in achieving their breastfeeding goals.
Objective: We aimed to survey personal breastfeeding experiences of faculty physician mothers who recently breastfed to help formulate a robust breastfeeding advocacy agenda. We hypothesized finding high incidence modifiable factors related to lactation support could improve physician breastfeeding goal success and ultimately improve the overall breastfeeding experience.
Design/Methods: An anonymous breastfeeding survey containing both quantitative and qualitative items was sent to female faculty physicians at an academic children’s hospital in 2020. Inclusion criteria included female faculty physicians who had given birth in the past 5 years. Of these, responses endorsing breastfeeding experience were analyzed.
Results: Fifteen percent of respondents stated that they did not meet their breastfeeding goals. The most prevalent theme for both positive and negative factors in the qualitative analysis was pumping breast milk. Physician mothers provided key insight into a) how the job role that is specific to a physician impacts breastfeeding experience, b) the impact of their return to work on breastfeeding, and c) ideas for improved lactation support. A limitation of our study was assessment at an academic pediatric institution resulting in respondents comprised of pediatricians and pediatric subspecialists who may have increased knowledge of the AAP’s recommendations regarding breastfeeding.
Conclusion(s): Our study highlights how differences in pumping experiences have a profound impact on the faculty physician’s perception of having either a positive or negative breastfeeding experience. Development of a more individualized breastfeeding support plan for each faculty physician, with attention to physical space and time accommodations for pump breaks is needed. We believe conversation surrounding lactation support between employer and the faculty physician should occur prior to maternity leave and continue at regular intervals upon return to monitor for changes in needs. This study echoes the need for ongoing efforts to improve maternal and infant health by advocating for faculty physicians who are providing breast milk for their child. Future studies should evaluate the benefit of advocacy and a detailed, individualized breastfeeding support plan developed as a result of this study.Presented at the 2021 PAS Virtual Conference
-

Differences in ED and Inpatient Utilization by Location of Primary Care: Co-location at a Head Start Center vs. Academic Primary Care Clinic Setting
Rupal Gupta and Jeffrey D. Colvin
Background: Children (ED) and inpatient utilization. Co-location of a primary care clinic within a Head Start center (HSC) includes nursing surveillance of classrooms and same-day primary care access, which allows students at the HSC to be seen immediately for acute care during the day. Consequently, co-location of primary care within a HSC may reduce barriers to acute care for those students, thereby lowering their ED and inpatient utilization.
Objective: To compare ED and inpatient utilization of students from a HSC with co-located primary care to patients treated at an academic primary care clinic (APCC).
Design/Methods: In this retrospective cross-sectional study, we compared ED and inpatient utilization from July 1, 2016 to June 30, 2019 for 278 children from a HSC with co-located primary care to a propensity score-matched comparison group of 810 patients receiving primary care at an APCC located 1.7 miles away. The main outcome was ED and inpatient utilization. ED utilization rate was dichotomized as <1/year and ≥1 visit/year. Inpatient utilization was dichotomized as 0 and ≥1 hospitalization during the study period. The main exposure was being a student at the HSC. A 3:1 comparison group was chosen using propensity score matching based on age, gender, race/ethnicity, language, and insurance type, with a strict match based on home census tract (i.e., every comparison patient lived in the same census tract as the matched HSC student). We used the X2test for bivariate analyses and logistic regression in our multivariable analyses.
Results: HSC and APCC patients had similar demographic characteristics (Table 1). A lower percentage of HSC students had an average of ≥1 ED visits/year than the comparison group (53.6% vs. 64.6%, p=0.001) (Table 2). There were no differences in hospitalizations. In comparison to having ≥1 ED visit/year, HSC students had 55% higher adjusted odds of having /year compared to the APCC group (aOR 1.55 [95% CI: 1.17, 2.06] p=0.002). There continued to be no differences in hospitalizations in our adjusted analyses (aOR 1.12 [95% CI: 0.73, 1.72] p=0.59).
Conclusion(s): Students from a HSC with co-located primary care had lower odds of having ≥1 ED visit/year compared to matched controls from an APCC. Future research should investigate cost differences, other health and developmental outcomes, and comparisons to private primary care practices.Presented at the 2021 PAS Virtual Conference
-

Educating Providers: Timely post-operative pain management in a Level IV Neonatal Intensive Care Unit (NICU)
Jamesia Donato, Darian Younger, Rebecca Palmer, Denise Smith, Alexandra Oschman, Meredith Kopp, Daphne Reavey, and Eugenia K. Pallotto
Background: NICU patients often encounter painful procedures and can have significant short and long-term consequences from inadequately treated pain. Ensuring adequate pharmacological and non-pharmacological pain management while minimizing associated risks is paramount. Our NICU is part of the Children’s Hospitals Neonatal Consortium “Erase Pain” collaborative to improve management of postop pain in neonates.
Objective: SMART
Aim: Increase the percentage of patients receiving acetaminophen within one hour after surgery to greater than 70% by July 2020.
Design/Methods: A multidisciplinary team developed pain treatment algorithms and postop order plans to standardize the approach to postop pain management. Providers were educated about their role in eliminating postop pain through mandatory educational sessions. Expectations include discussing pain management plan on rounds and during pre and postop team handoffs, utilize standard pain treatment algorithms (Fig.1) and order plans (Fig. 2). The order plan prioritizes the acetaminophen order to STAT, to support administration within the first hour after return from surgery. Process measures include compliance with use of the post op pain algorithm and order plan. Baseline data was reviewed from January-July 2019 and post education data obtained August 2019-August 2020.
Results: Provider compliance with the order plan improved from a baseline of 16.7% of patients before education to 77.3% after intervention. Acetaminophen was administered within the first hour postoperatively more often after provider education, improving from a baseline of 41% to 74.7%. The percentage of patients receiving acetaminophen within the first hour was greater than 70% by July 2020 which precisely achieved our SMART AIM, shifts our center line (Fig. 3 and Fig 4) and is attributed to correct use of the order plan and algorithm. The percentage of elevated pain scores, monitored as a balancing measure, increased during this time period. Opioid exposure review as a balancing measure is ongoing.
Conclusion(s): Educating providers about the importance of discussing postop pain and administering multimodal analgesia is effective in improving ordering practices and timely acetaminophen administration. With an increase in the percentage of elevated pain scores, addressing additional system factors is needed for optimal post-op pain treatment. Future aims include investigating events contributing to delayed acetaminophen administration and implement interventions to improve pain management.Presented at the 2021 PAS Virtual Conference
-

Efficacy and Safety of Bardoxolone Methyl in Pediatric Patients with Alport Syndrome in CARDINAL Phase 3 Trial
Bradley A. Warady, Sharon Andreol, Vimal Chadha, Melanie Chin, Rasheed Gbadegesin, Keisha Gibson, Debbie Gipson, Angie Goldsberry, Kenneth Lieberman, Colin Meyer, Kevin Meyers, Nozu Kandai, Megan O'Grady, Michelle Rheault, and Clifford Kashtan
Background: Alport syndrome accounts for an estimated 3% of children with end-stage kidney disease in the US (USRDS, 2014). Whereas current management recommendations include the use of renin-angiotensin-aldosterone system inhibitors (RAASi) in patients with proteinuria, no specific therapies have been approved for this disease.
Objective: A Phase 3 study (CARDINAL; NCT03019185) evaluated the safety and efficacy of bardoxolone methyl (Bard) in adult and adolescent patients with Alport syndrome.
Design/Methods: CARDINAL was an international, multicenter, double-blind, placebo-controlled, randomized trial conducted over two years in patients with confirmed diagnosis of Alport syndrome. Patients aged 12 to 70 years old with baseline eGFR 30-90 mL/min/1.73 m2 and urinary albumin to creatinine ratio (UACR) ≤ 3500 mg/g were randomized 1:1 to Bard or placebo. Patients did not receive study drug during a 4-week withdrawal period between Weeks 48 and 52, after which treatment was re-started and continued through Week 100. Efficacy endpoints for all patients were changes from baseline in eGFR in Bard-treated patients relative to placebo at Weeks 48 and 100 (primary) and at Weeks 52 and 104 (key secondary), following a 4-week withdrawal period.
Results: A total of 23 (15%) pediatric patients were randomized in the trial. The average age at screening for these patients was 15.3 years, mean (± SD) baseline eGFR was 69.9 ± 15.4 mL/min/1.73 m2 and mean (± SE) baseline UACR was 230.9 ± 95.8 mg/g. A total of 14 of 23 (61%) patients had an X-linked mode of inheritance, 6 (26%) patients had autosomal disease. Four (17%) patients were female, and 17 (74%) patients received RAASi treatment.
In pediatric patients, Bard treatment resulted in a significantly higher mean change from baseline in on-treatment eGFR compared to placebo at Week 100 (13.8 mL/min/1.73 m2; p = 0.0017), and in off-treatment eGFR compared to placebo at Week 104 (14.6 mL/min/1.73 m2; p = 0.0035), despite mean UACR remaining generally unchanged. Mean body weight in Bard-treated pediatric patients also remained generally unchanged relative to baseline through Week 100. No serious adverse events (AEs) were reported in Bard-treated pediatric patients and reported AEs were consistent with those observed in previous studies.
Conclusion(s): In CARDINAL, the addition of Bard to RAASi in pediatric patients with Alport syndrome and chronic kidney disease appeared to preserve kidney function and was generally well-tolerated.Presented at the 2021 PAS Virtual Conference
-

Evaluation of the hypothesis that viral meningitis is a mimic of abusive head trauma
Danielle Horton, Tanya Burrell, James Anderst, Lyndsey Hultman, Mary Moffatt, Henry T. Puls, and Rangaraj Selvarangan
Background: Viral meningitis (VM) has been proposed as an alternative cause of subdural hemorrhage (SDH) in young children diagnosed with abusive head trauma (AHT). It has been proposed that VM may mimic symptoms and clinical features of AHT, resulting in an incorrect diagnosis of abuse.
Objective: We aim to evaluate the hypothesis that VM is a mimic of AHT by comparing the history of present illness (HPI) and initial clinical presentation of young children with proven VM to those with subdural hemorrhage and concomitant suspicious injuries (SDH + CSIs) and to those with SDH and no CSIs (SDH only). We hypothesized that significant differences would exist between the VM group and the other two groups.
Design/Methods: We performed a 5-year retrospective case-control study of subjects < 2 years of age comparing those with PCR- confirmed VM (controls) to those with SDH who were evaluated by the hospital Child Abuse Pediatrics (CAP) team (cases). Historical and clinical features were obtained from the Emergency Department and admission notes only. Cases were classified as those with and without one or more CSI. Using Chi-Square test, Fisher’s Exact Test and Mann-Whitney U Test, groups (VM, SDH with CSI, SDH only) were compared across 3 domains: demographics (5 measures), caregiver reported history (20 measures), and clinical (15 measures).
Results: Of 550 subjects, 397 had confirmed VM, 118 had SDH + CSI and 35 had SDH only. The VM subjects differed significantly from SDH + CSI subjects on all demographic measures, and from SDH only subjects on one measure (age). In the history domain, VM subjects differed significantly from SDH + CSI subjects in 18 of 20 measures with odds ratios (ORs) ranging from 2.7 to 322.5. VM subjects differed significantly from SDH only subjects in 12 of the 20 history measures, with ORs ranging from 4.6 to 485.2. In the clinical domain, VM subjects differed significantly from SDH +CSI subjects in 11 of 15 measures, with ORs ranging from 2.5 to 74.0. VM subjects differed significantly from SDH only subjects in 6 of 15 clinical measures with ORs ranging from 2.9 to 16.8. The combined findings of a history of acute mental status change and absence of fever were seen in 62.7% of the SDH + CSI subjects, 45.7% of the SDH only subjects, and 1% of the VM subjects. Using the SDH + CSI group as a proxy for abuse, this combination of features had a positive predictive value (PPV) of 95% for abuse.
Conclusion(s): Viral meningitis is not supported as a mimic of abusive head trauma.Presented at the 2021 PAS Virtual Conference
-

Gender Dysphoria, General Well-Being, BMI, and Weight-Related Behaviors among Adolescent Transgender Males
Timothy A. Roberts, Anna Egan, Mirae J. Fornander, Christine Moser, and Michaela Voss
Background: Gender dysphoria is associated body-dissatisfaction, abnormal weight and weight-related behaviors.
Objective: Describe the association of gender dysphoria severity and general well-being with Body Mass Index (BMI) and weight related behaviors among transgender males.
Design/Methods: Retrospective review of 118 transgender male patients presenting to initiate gender-affirming medical care in 2017-2020. Gender dysphoria confirmed by an experienced mental health provider. We measured parent and patient reports of patient general well-being [Pediatric Quality of Life Inventory (PedsQL) 4.0 General Well-Being Scale], severity of gender dysphoria [Transgender Congruence Scale (TCS) [n=47 for TCS] and Gender Identity/Gender Dysphoria Questionnaire (GIDYQ-AA)], weight related intentions, and weight related behaviors.
Results: Mean age 15.7+/-1.5 (range 10.0-19.2) and race/ethnicity- 88.8% White, 7.8% multiracial/other, 2.6% Hispanic, and 0.9% Black. Mean BMI Z-score 1.05+/-1.11. 0.8% of patients had a BMI <5th%tile, 22.9% 85-95th%tiles, and 22.0% >95th%tile. Most patients reported they were about the right weight (42.6%) or slightly overweight (35.2%). 40.4% denied weight-related intentions and 43.1% were trying stay the same weight. 8.6% reported fasting and 2.6% purging to control weight during the previous 30 days. Mean parent PedsQL=63.5+/-15.6 and patient PedsQL=64.3+/-14.3. Parent-Child PedsQL correlation 0.471. Mean dysphoria scores: TCS=2.72+/-0.62 and GIDYQ-AA=1.98+/-0.24.
Lower parent PedsQL scores were associated with higher BMI Z-scores and more patient reports of perceiving the themselves to be overweight and fasting to lose weight. Patient PedsQL General Well Being Scores were not associated with any of our outcomes. Severity of gender dysphoria had a quadratic relationship with BMI (TCS: R2 0.169, Pearson correlation -0.403; GIDYQ-AA: 0.051, -0.227) with higher and lower levels of gender dysphoria associated with a lower BMI Z-score. The relationship between Parent PedsQL and BMI Z-score was no longer significant after adjusting for TCS score.
Conclusion(s): Lower parent PedsQL Well Being scores are associated with increased BMI, self-perception of being overweight, and fasting to lose weight. There is a non-linear relationship between gender dysphoria and BMI. Further research is needed to determine if the non-linear relationship between dysphoria and BMI is present in other transgender youth and associated with differences in weight-related behaviors.Presented at the 2021 PAS Virtual Conference
-

Household income, psychosocial stressors, and risk factors for sleep-related infant deaths
Jeffrey D. Colvin, Isabella Zaniletti, Carolyn Ahlers-Schmidt, Vicki Collie-Akers, Christy Schunn, Rosemary Nabaweesi, Debbie Cheney, and Rachel Y. Moon
Background: Sleep-related infant deaths (e.g., SIDS, accidental suffocation, undetermined) are the leading cause of postneonatal mortality. Infants from low income families have higher rates of sleep-related deaths. Other risk factors for sleep-related death include nonsupine sleep position, bedsharing, maternal smoking, sleeping in separate room, soft bedding, and breastfeeding <8 weeks. Little is known about how these risk factors vary by income or if psychosocial>stressors, social services, and education of parents from healthcare providers about risk factors influence these risks among low income families.
Objective: Aim 1: Describe differences in risk factors for sleep-related infant death by family income. Aim 2: Among low income families, describe differences in risk factors by psychosocial stressors, services, and risk-factor education.
Design/Methods: We analyzed 2016-2017 CDC Pregnancy Risk Assessment Monitoring Study (PRAMS) data in 47 states. PRAMS questions mothers of infants regarding infant sleep practices, smoking, income, psychosocial stressors (e.g., financial stress, domestic violence), services (e.g., WIC), and risk-factor education. The main predictor for Aim 1 was household income. For Aim 2, the main predictors were psychosocial stressors, services, and risk-factor education. Table 1 details the variables used. The main outcomes were risk & protective factors: (1) sleep position, (2) sleep surface, (3) sleep location, (4) soft objects in sleep area, (5) breastfeeding duration (<8 weeks vs>≥8 weeks), and (6) maternal smoking. We used the X2 test for bivariate analyses and multivariable logistic regression for adjusted analyses.
Results: There were 1.8 million weighted respondents. For Aim 1, mothers with low income mothers had 12x higher odds of roomsharing without bedsharing, 96% lower odds of breastfeeding ≥8 weeks and >99% lower odds of living in a smoke-free household (Tables 2 & 3). For Aim 2, domestic violence during pregnancy and certain stressors were associated with ~50% increased odds of maternal smoking (Table 4). Domestic violence also had 50% decreased odds of using a separate approved sleep surface. Receipt of education on sleep position and sleep location had 2.5x increased odds of a safe sleep position and ~30% increased odds of roomsharing without bedsharing.
Conclusion(s): To decrease income disparities in sleep-related infant deaths, interventions should support breastfeeding and smoking cessation, as well as address domestic violence and specific stressors, in low income families.Presented at the 2021 PAS Virtual Conference
-

Human Lactoferrin and the Siderophore Aerobactin Independently Impact Intestinal Invasion by Neonatal Escherichia coli Bacteremia Isolates
Susana Chavez-Bueno, Joshua Wheatley, and Jennifer Tabakh
Background: E. coli is a major cause of neonatal sepsis. After ingestion, E. coli translocates the neonatal gut causing bacteremia. E. coli virulence depends on iron acquisition mechanisms, including siderophore systems. Lactoferrin (LF) protects against neonatal sepsis through immunomodulatory and antimicrobial effects which include iron chelation. However, it is not known whether siderophores in neonatal E. coli strains have an impact on LF’s effects on bacterial invasion and survival in intestinal epithelium.
Objective: To investigate the effects of human LF and the siderophore aerobactin on intestinal invasion and survival of septicemia-producing neonatal E. coli.
Design/Methods: Neonatal E. coli septicemia isolates RS218 and SCB34, and the nonpathogenic laboratory strain DH5α were first compared in their ability to grow in liquid media with 1 mg/mL human lactoferrin (LF) by measuring optical density over 20 h at 37°C. A deletion mutant in SCB34 lacking the aerobactin siderophore receptor gene iutA (ΔiutA) was also tested. Invasion of T84 intestinal epithelial cells was compared between SCB34 and ΔiutA using a gentamicin protection assay, substituting amikacin due to the strain’s resistance profile. Invasion was assessed in the presence of 1 mg/mL LF at the time of infection, and also after overnight incubation of T84 cells with 1 mg/mL LF.
Results: RS218, SCB34 and ΔiutA grew similarly without LF, but significantly less in the presence of LF (Fig. 1, P<0.001). This effect was greatest on DH5α. Invasion and recovery of live bacteria from within T84 intestinal cells was no different between SCB4 and ΔiutA when LF was added at the time of infection, confirming that E. coli does not undergo substantial growth prior to invasion in this model (not shown). Conversely, LF pretreatment of T84 cells prior to E. coli invasion significantly reduced the recovery of live SCB34 (Fig. 2, P=.012). Moreover, invasion by ΔiutA in LF-untreated T84 cells was significantly reduced compared to SCB34 (P=.016), but did not significantly decrease in the presence of LF.
Conclusion(s): LF significantly impairs growth of neonatal E. coli clinical isolates but does not completely abolish it. While LF also decreased neonatal E. coli invasion, the effect was independent of the function of the siderophore aerobactin, which by itself is necessary for invasion. The iron-dependent mechanisms determining host-E. coli interactions are potential therapeutic targets against neonatal sepsis.Presented at the 2021 PAS Virtual Conference
-

Impact of Early Tracheostomy on Neurodevelopmental Outcome of Infants with Severe Bronchopulmonary Dysplasia Exposed to Postnatal Steroids
Amjad Taha, Gangaram Akangire, Janelle R. Noel-Macdonnell PhD, Tiffany Willis, and Winston M. Manimtim
Background: BPD is associated with neurodevelopmental impairment. Tracheostomy is performed in 5-12% of severe BPD for prolonged ventilation. There is evidence that chronic ventilation with tracheostomy in severe BPD may facilitate neurodevelopment and lead to improved outcome. However, there is no consensus on the optimal timing of tracheostomy. A large multicenter study of infants with tracheostomy performed at <120 days of life had better neurodevelopmental outcomes at 18-22 months of age. Use of steroids postnatally to ameliorate the severity of BPD had been controversial due to its negative effect on neurodevelopment. To>date, no data has specifically evaluated the impact of early tracheostomy on neurodevelopmental outcome of infants with severe BPD who are exposed to postnatal steroids.
Objective: To compare cognitive, language and motor scores among 3 groups of severe BPD infants who received early vs late vs no tracheostomy. Secondly, evaluate if postnatal steroids had an additive negative effect on neurodevelopmental outcomes.
Design/Methods: IRB approved retrospective cohort of infants with severe BPD in a level IV NICU and followed in neonatal follow up clinic, 2010–2017, grouped into early (ET) <121 >days, late (LT) >121 days and no tracheostomy (NT). Primary outcome: cognitive, language and motor developmental scores at 2-3 years of age, by Bayley Scales of Infant and Toddler Development, 3rd edition. Secondary outcome: compared cumulative steroid exposure among 3 groups.
Results: N=68. 41(60%) had tracheostomy and 27 (40%) with no tracheostomy. Median age at tracheostomy 121 days, 22 (54%) had ET, 19 (46%) had LT. Demographics shown in Table 1. Kruskal Wallis test (nonparametric ANOVA) showed significant difference in motor composite scores in ET vs LT (median score 85 vs 73, p 0.028). A trend for better cognitive scores in ET vs LT vs NT but not significant. No difference in language scores among the 3 groups. Overall, LT group had the lowest scores in all three domains (Figure 1). LT group had the most steroid exposure while the NT had the least (Median steroid cumulative exposure calculated as hydrocortisone equivalent in mg: 595.05 (67.50, 1213.60); 347.20 (132.95, 677.00); 97.90 (35.60, 237.50); p=0.012) respectively.
Conclusion(s): Early tracheostomy may improve neurodevelopmental outcome in severe BPD particularly in motor domain. Delaying tracheostomy in severe BPD may predispose to more postnatal steroids exposure and possible worst neurodevelopmental impairment.Presented at the 2021 PAS Virtual Conference
-

Improving Access to Spanish COVID-19 Resources at a Children’s Hospital
Fernando Zapata, Romina Barral, July K. Jean Cuevas, Lines Vargas Collado, Nicholas Clark, Amanda Montalbano, and Cristina Fernandez
Background: The COVID-19 pandemic disproportionately impacts Spanish-speaking communities. COVID-19-related health information is overall more available in English than Spanish. From May to August 2020, Spanish COVID-19-related resources on our institution’s website had an average of 2954 views/month compared to 48573 views/month to the English COVID-19-related resources.
Objective:
Our project aim was to increase the percent of page views for Spanish COVID-19-related resources on our institution’s website from 5.7% of the total views to the COVID-19-related pages, to 20% from September 2020 through June 2021.
Design/Methods: An ethnically diverse, multidisciplinary team including physicians proficient in Spanish as well as our institution’s information technology, marketing, and public relations departments used improvement methodology to identify root causes using a driver diagram to guide interventions. Outcome measure was percent of page views to the Spanish COVID-19 website out of all COVID-19 website views (Spanish and English). The total number of Spanish COVID-19 website views served as the process measure. Plan-Do-Study-Act cycles were developed: 1) All COVID-19 information was translated to Spanish (September); 2) Recorded and aired educational video on a local Spanish television station regarding Spanish COVID-19 resources available on the website (October); 3) Addition of QR Code linking to the Spanish COVID-19 website on clinic discharge paperwork (November); 4) Rerun video on local Spanish television station, with a new Holiday Tips and Safety video and a direct link added to their website (December). Run and control charts were utilized to assess improvement over time.
Results: Process measure improved from a mean of 2954 monthly views to 3803 during the intervention period while at the same time English COVID-19 website page views decreased from a mean of 48558 to 40321 monthly page views (Fig 1). During the intervention period, outcome measure displayed special cause improvement from 5.7% to 8.7% of total COVID-19 page views arising from Spanish COVID-19 websites (Fig 2).
Conclusion(s): QI methodology revealed a lack of Spanish resources on our institution’s website and underutilization in accessing them. Interventions included improving the quality and content and disseminating the information internally and externally. The project has been successful in increasing traffic to Spanish COVID-19 resources. QI methodology can be used to help close gaps in pandemic-related health disparities.Presented at the 2021 PAS Virtual Conference
-

Improving the Rate of Emergency Department Physician Pre-Procedure Time-Out Documentation for Deep Sedation and Cutaneous Abscess Incision and Drainage
Arjun Sarin, Nikita Sharma, and Shobhit Jain
Background: The pre-procedure time-out, an important safety measure to verify patient identity and accuracy of a planned procedure, and Joint Commission requirement, is not documented consistently by physicians in our emergency department (ED). Deep sedation and cutaneous abscess incision and drainage (I&D) are two high-risk procedures performed in the ED, supporting the use of a time-out in this setting. Between June 2018 and May 2019, a pre-procedure time-out was documented in the physician procedure note of the electronic medical record (EMR) for 75% of deep sedations, and 94% of I&Ds.
Objective: We aimed to improve ED physician pre-procedure time-out documentation for deep sedation (ketamine and/or propofol) from 75% to 90%, and I&D from 94% to 98% by July 2020.
Design/Methods: Our ED is part of a free-standing, tertiary children’s hospital, comprised of two separate locations across two states, with a combined annual volume of 125,000 visits. We analyzed one year of baseline data for deep sedations and I&Ds performed in both locations, followed by weekly reports from November 2019 to July 2020. We provided education to the physicians regarding the history and importance of the pre-procedure time-out, monthly reminders and updates, as well as individualized feedback for deficient documentation. We optimized EMR procedure notes for deep sedation and I&D, and incentivized the project with American Board of Pediatrics Maintenance of Certification (MOC) credit, as well as a financial bonus. For cases of concurrent deep sedation and I&D, we expected the time-out be documented in both of the independent procedure notes, and measured these accordingly.
Results: During the study period we averaged 100 deep sedations and 25 I&Ds per month. Physician documentation of a pre-procedure time-out improved from 75% to 100% for deep sedation, and from 94% to 99.3% for I&D. The improvements remained sustained for five months without additional intervention. All physicians were eligible for the financial bonus; 40 met MOC credit requirements.
Conclusion(s): A pre-procedure time-out may reduce the likelihood of avoidable patient harm and is practical to perform in a busy ED setting. Using quality improvement methodology, we increased ED physician pre-procedure time-out documentation for deep sedation and I&D through education, feedback, and systems improvement. Future studies may quantify the effects on patient safety and examine the use of similar interventions for other ED procedures.Presented at the 2021 PAS Virtual Conference
-

Learning From the Past: A Novel and Sustainable Initiative to Reducing Unplanned Extubations in a Level IV Neonatal Intensive Care Unit
Yonatan Kurland, Dena Hubbard, and Eugenia K. Pallotto
Background: Unplanned extubations (UPEs) are a cause of significant morbidity and mortality in neonates. Multiple successful interventions had been previously implemented in our NICU including standardized endotracheal tube (ETT) securement procedures, bedside checklists, and multi-disciplinary debriefing. In our unit greater than 65% of UPEs occur in neonates under 1.5kg who are particularly sensitive to small adjustments in tube position. We designed a novel approach to reducing UPEs in this patient population.
Objective:
Design/Methods: We hypothesized that increased awareness of historical ETT position would both prevent unnecessary ETT position adjustments and encourage prophylactic adjustments to adjust for significant weight gain or loss. In December 2019, we implemented a novel intervention to provide readily accessible graphs of historical ETT tube position in each neonate with corrected gestational age <32 weeks. In successive>cycles, education was provided to all members of the multidisciplinary team, the graph was refined into a readily printable format and changes were made to the unit workflow to ensure updated graphs were available at the bedside at every shift.
Results: UPE rates in 2019 prior to the intervention were 1.0 events per 100 vent days. In the 12 months following the intervention and refinements, the UPE rate decreased to 0.76 per 100 vent days. Balancing measures included the frequency of tube position changes, tube re-taping and chest x-rays which did not change or showed a decrease over the study period.
Conclusion(s): By providing ready access to information on historical ETT position, our unit fostered an environment of communication & safety with a sustained and decreasing rate of unplanned extubations.Presented at the 2021 PAS Virtual Conference
-

Medical Neglect: Trends in Reporting Practices and Patient Characteristics
Danielle Horton, Emily Killough, and Mary Moffatt
Background: Medical neglect has significant consequences on child health and well-being. Improved processes for defining, recognizing, and reporting medical neglect are needed, however there is limited published data on the subject. Insight into patient characteristics and current reporting practices will help identify areas for intervention to improve outcomes for children at risk for medical neglect.
Objective: To describe characteristics of children identified for concern of medical neglect and trends in reporting of cases to child protective services (CPS).
Design/Methods: We performed a 1-year retrospective descriptive study of subjects < 18 years of age at a single, tertiary-care, academic pediatric institution for whom a Patient at Risk (PAR) assessment was completed exclusively for the concern of medical neglect. The PAR is a unique institutional process by which health professionals and social workers document concerns for child maltreatment. Medical records were reviewed for data regarding demographics, medical history, health care utilization and psychosocial risk factors. The role of the initiating provider and healthcare setting in which the PAR was recorded were also obtained.
Results: Of 270 children with a PAR completed for medical neglect concerns, 97.4% were reported to CPS. PARs were most frequently initiated in the ambulatory (60.7%) setting by physicians (43%) or social workers (28.5%). Missed ambulatory appointments were common, with 62.2% of subjects having more than 5 missed appointments since establishing care. Chronic medical conditions were present in 80% of subjects. Over half (53%) of subjects had prior known involvement with CPS and 20% of subjects had a prior PAR completed for concern of medical neglect. Subjects were primarily African American (40%) or Caucasian (38.9%) and the majority were publicly insured (80.4%). Over half (59.6%) of subjects had at least 1 of 5 psychosocial risk factors addressed in PAR assessments (caregiver substance abuse, mental health issues, incarceration; intimate partner violence; transportation or financial challenges).
Conclusion(s): Concerns for medical neglect are most frequently identified in the ambulatory care setting. Chronic medical conditions and psychosocial risk factors that may create a barrier to care are common. Data informed next steps include systemic monitoring of missed ambulatory clinic appointments and design of a standardized process to improve consistency of diagnosis and intervention in cases of medical neglect for children with chronic medical conditions.Presented at the 2021 PAS Virtual Conference
-

Multimodal Pain Control in Common Neonatal Surgeries: Post-operative Pain Protocol Reduces Opiate Exposure and Side Effects
Jamesia Donato, Nefertari Terrill-Jones, Ashley K. Sherman, Warren Teachout, Stephanie Prince, Alexandra Oschman, Daphne Reavey, Darian Younger, and Tamorah R. Lewis
Background: Opioids are the primary post-operative (post-op) analgesic in neonates. Side effects include hypotension, apnea and ileus. Previous studies show IV acetaminophen decreases opiate need in specific populations including cleft palate repair, cardiac surgery. The effect of IV acetaminophen as part of a post-op pain algorithm is not known in common neonatal surgical procedures.
Objective: To determine if (a) a post-op pain algorithm including IV acetaminophen and (b) IV acetaminophen exposure reduces cumulative opioid requirements in neonates undergoing common surgeries in the NICU.
Design/Methods: This is a retrospective cohort study comparing cumulative post-operative opiate exposure between infants with common surgeries in two cohorts: pre-pain algorithm (2013-2015, “PRE”), post-pain algorithm (2016-2018, “POST”), and also between infants who received post-op IV acetaminophen versus did not. Cumulative doses in IV Acetaminophen and opioids were calculated for each patient in the72 hours post-op. Pain scores, respiratory depression, hypotension, time to extubation, time to first stool, and time to enteral feeds were secondary outcomes. Wilcoxon Rank Sum tests were used for outcome comparisons amongst groups.
Results: 690 infants met inclusion criteria. 306 (44%) patients were PRE and 384 (56%) POST. In the entire cohort, 202 patients (29%) received IV acetaminophen post-operative and 488 (70.7%) did not. PRE and POST median 72 hours opiate exposures were 0.56 mg (IQR 0-1.4) and 0.18 mg (IQR 0-0.82) respectively, p <0.01. Acetaminophen vs. non-Acetaminophen recipients had median opiate exposure of 0.30 mg (IQR 0-1.10) and 0.33 mg (IQR 0-1.2) respectively, p = 0.6245). Post-operative hypotension was 46.6% in PRE and 26.4% in POST (p <0.01); 27.9% and 38.5% in acetaminophen versus non-acetaminophen respectively (p = 0.01). Acetaminophen recipients had significantly higher pain scores (p <0.01). Median hours intubated was less in POST (22.3 hr, IQR 8.1-38.9) vs. PRE (25.8, IQR: 17.7-44.1); p < 0.01. Time to first stool was similar amongst all groups.
Conclusion(s): Implementation of a post-op pain algorithm in the NICU significantly reduced cumulative opioid exposure. Hypotension and intubation time were reduced with acetaminophen exposure. With an increase in the percentage of elevated pain score in the group receiving IV acetaminophen, addressing additional system factors is needed for optimal postoperative pain treatment.Presented at the 2021 PAS Virtual Conference
-
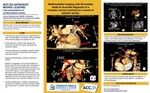
Not-so-apparent Mixing Lesions: Late Presentation Of Cardioembolic Stroke
Amulya Buddhavarapu, Christopher Mathis, William Gibson, and Sanket Shah
Background: Multiple levels of inter-atrial shunting can rarely present late in life with dyspnea and embolic stroke from effects of bidirectional shunting.
Case: A 55-year-old male with history of a patent foramen ovale, atrial fibrillation and embolic stroke presented with worsening fatigue and dyspnea at rest. Echocardiogram showed mildly reduced ventricular function with severe right heart dilation. On transesophageal echo, the coronary sinus (CS) was severely dilated with a persistent left superior vena cava (LSVC). A stress test showed no perfusion defects. CT angiography showed an absence of right SVC and a single LSVC connecting to the CS. There was partial anomalous pulmonary venous connection of the left upper pulmonary vein to the LSVC. The left lower pulmonary veins connected to the left atrium (LA) but largely drained indirectly to the right atrium via a defect at the LSVC-CS junction. The right pulmonary veins returned normally to the LA.
Decision‐making: Catheterization revealed pulmonary overcirculation with pulmonary to systemic flow ratio [Qp:Qs] of 2:1. Surgery was preferred over percutaneous intervention for the repair of atrial septal defects and redirection of left upper pulmonary venous return to the left atrial appendage. The patient improved significantly following surgery.
Conclusion: Multimodality imaging can help accurately diagnose venous anomalies and create three-dimensional models instrumental in procedural/surgical planning.
-

Online Echocardiography Modules for Pediatric Cardiology Fellows
Sarah Studyvin, Doaa Aly, Laura Kuzava, Tyler Johnson, Alison Samrany, Nitin Madan, and Sanket Shah
Background: Adequate echocardiographic (echo) education is integral to successful cardiology training. Online education is proven to be effective in other specialties, but pediatric echo training data are lacking. Our aim was to design and assess the role of a novel online module-based curriculum to enhance pediatric cardiology fellows’ echo education.
Methods: Four interactive modules, focused on principles and interpretation of a normal echo, were delivered to fellows. Content included high quality 2D and 3D echo clips (Fig 1A) as well as interactive quizzes (Fig 1B) and could be accessed from a phone, tablet, or computer. All fellows completed pre- and post-tests, validated by independent expert imagers, and surveys.
Results: 100% of fellows (n=7) participated in the pilot study. Test scores improved after completing the modules, and most fellows maintained a higher score at 4-weeks, suggesting good knowledge retention (Fig 1C). Self-assessed confidence in echo knowledge and interpretation, as assessed on a numeric scale, also improved (Fig 1D).
Conclusion: Online microteaching modules can provide a valuable adjunct to traditional echo education in cardiology fellowships. Our digital, phone-accessible curriculum was well received by fellows and was associated with an objective and subjective improvement in their understanding and interpretation of a normal echo. Further expansion of such modules will be beneficial in the evolving era of virtual education in the face of the COVID-19 pandemic



