These posters have been presented at meetings in Children's Mercy and around the world. They represent research that was done at the time they were created, and may not represent medical knowledge or practice as it exists at the time viewers access these posters.
-

Outpatient Antimicrobial Stewardship Programs in Children’s Hospitals: Status, Needs, Barriers
Rana El Feghaly, Elizabeth Monsees, Alaina N. Burns, Brian Lee, Ann L. Wirtz, Adam L. Hersh, and Jason Newland
Background: Antimicrobial stewardship programs (ASPs) are an essential tool to combat the increasing threat of antibiotic resistance. ASPs traditionally reside in acute care settings with a focus on inpatient prescribing. However, in 2016, the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention affirmed the importance of outpatient ASP through its 4 core elements. Incorporation of these elements requires time, personnel, and funding, which may not be available in many institutions.
Objective: This study aimed to evaluate the current state of outpatient ASP in a large network of children’s hospitals and inform a programming agenda.
Design/Methods: This cross-sectional study used an investigator-developed survey to assess current resources, interventions, and obstacles of outpatient ASP. We invited institutions from the Sharing Antimicrobial Reports for Pediatric Stewardship OutPatient collaborative (SHARPS-OP), which includes 54 sites from the United States and 2 from the United Kingdom. We used descriptive statistics to examine institution characteristics, current outpatient ASP work, and elucidate collaborative goals.
Results: Forty-five sites participated achieving an 80% (45/56) response rate. Only 5 sites (11%) had allocated support for outpatient ASP, although 42 (95.6%) had allocated support for inpatient ASP (Table 1). The most widely used ASP interventions included toolkits (57.8%), education (46.7%), quality improvement projects (37.8%), research (27.8%), and electronic medical record features (27.8%) (Table 2). Time was identified as the biggest barrier to outpatient ASP (91%) followed by financial support (53%), development of meaningful reports (51.1%), and administrative support (44.4%). The most important goals of the collaborative included benchmarking and developing clear metrics for pediatric outpatient ASP (Table 3). Optional comments were provided by 93% of respondents indicating multiple areas of program needs which were condensed into 6 themes (Table 4) primarily focused on securing operational support (36%) and strengthening data analysis (31%). Likewise, data analysis was the most frequently cited request for collaborative discussion.
Conclusion(s): Most institutions had robust acute care support and appreciated the urgent need to address outpatient antibiotic use. Only a small number of participants had allocated support to secure the progression of outpatient ASP with data analysis being a universal program need.Presented at the 2021 PAS Virtual Conference
-

Parental Health Literacy and Acute Care Utilization in Children with Medical Complexity
Emily J. Goodwin, Joy L. Solano, Jessica L. Bettenhausen, Ryan Coller, Adrienne G. DePorre, Rupal Gupta, Kayla R. Heller, Lauren Jones, Leah Jones, Kathyrn Kyler, Ingrid Larson, Laura Plencner, Margaret Queen, Timothy Ryan Smith, Tyler Smith, Jacqueline M. Walker, Margaret Wright, Isabella Zaniletti, and Jeffrey D. Colvin
Background: Inadequate health literacy, defined as inadequate ability to find, understand and use health information is associated with poor health outcomes and high health care costs. Children with medical complexity (CMC) have high rates of acute care utilization. Understanding parental health literacy in CMC and its relationship to acute care utilization may inform interventions designed to lower utilization.
Objective: To examine parental health literacy for CMC and determine its association with acute care utilization.
Design/Methods: In this single-site cross-sectional study, 250 parents of CMC completed a self-administered survey (response rate of 66.1%). CMC were included if they had a complex chronic condition (CCC) and were enrolled in the CMC primary care clinic or received primary care at the study site. The main predictor was parental health literacy as measured by the validated Single Item Literacy Screener (SILS). SILS measures the frequency of needing assistance when reading medical information. Table 1 lists the categorization of SILS responses in our original and post hoc analyses. Main outcomes were acute care utilization defined as annual emergency department (ED) visits, hospitalizations, and associated costs. We examined bivariate associations with the X2 test and multivariable associations with a generalized linear model with log link and time from first to last episode as offset, adjusting for demographic and clinical characteristics.
Results: About 94% of parents had adequate health literacy (Table 2). Adequate health literacy increased with the number of CCCs (p<0.01). When using the traditional categorization of SILS responses, there were no differences in acute care utilization by health literacy in the bivariate (Table 3) and adjusted analyses (Table 4). In the post-hoc adjusted analyses, parents with Low-Adequate health literacy had seven times greater annual ED costs compared to parents with High-Adequate health literacy. They also had 35% more annual hospitalizations and 64% greater hospitalization costs compared to parents with High-Adequate health literacy (Table 4).
Conclusion(s): Parents of CMC had high rates of adequate health literacy. Future studies should determine if this is common in parents of CMC or unique to our study population. We found few associations with acute care utilization. Future studies should examine if additional aspects of health literacy (e.g., listening, speaking, numeracy) not included in the SILS better predict acute care utilization.Presented at the 2021 PAS Virtual Conference
-

Pediatric Resident Reflections from a Non-Medical Home Visit of a Child with Medical Complexity
Emily J. Goodwin, Sheryl Chadwick, DeeJo Miller, Kathryn Taff, and Amanda Montalbano
Background: Pediatric residents typically only interact with patients and families in healthcare settings which limits the opportunity to fully understand the patient and family experience. Encounters with children with medical complexity (CMC) that only relate to illness or health monitoring can anchor residents to false preconceptions and limit their ability to practice patient- and family-centered care (PFCC). The core principles of PFCC include acknowledging patient and family expertise and strengths, encouraging their input, and appreciating the value of their observations and perceptions.
Objective: To explore how a home visit program with patients and families serving as faculty could instill the principles of PFCC in pediatric residents.
Design/Methods: This mixed methods study used grounded theory to qualitatively analyze 10 years of retrospective data from resident reflections facilitated by parents on staff following a non-medical home visit with a CMC. Transformative and social learning theories were used to structure the output into 6 themes: frame of reference, observations, realizations, disorienting dilemmas, reflections and discourse, and shifts in their world view.
Results: The 132 reflection sessions were analyzed using a 90-word code book to capture 11,194 codes in 3,741 excerpts. Responses early in the reflection sessions most often were more factual statements representing their prior attitudes and experiences, literal observations from the home visit, and discovery of new knowledge. By the end of the sessions the excerpts represented challenges to their preconceptions, shifts in their frames of reference, and comments about how this experience will alter or impact their future practice (Table 1). The most common codes reflected the PFCC principles including “normalcy,” “family centered care,” and “medicine beyond the bedside.”
Conclusion(s): Immersion experiences solidify or alter resident frames of reference; however, a facilitated group debrief may deepen the learning opportunity and lead to a variety of realizations that promote broader reflections and discourse. Parent facilitated reflection sessions following a non-medical home visit instilled concepts that are difficult to teach within clinical settings.Presented at the 2021 PAS Virtual Conference
-

Perinatal exposure to Interleukin-6 (IL-6): a model to study influence of developmental insult on susceptibility to chronic kidney disease (CKD)
Tarak Srivastava, Robert E. Garola, Varun Chandra Boinpelly, Jianping Zhou, Daniel P. Heruth, Mohammad Rezaiekhaligh, M. Farhan Ali, Lakshmi Priya, Uri Alon, Trupti Joshi, Yuexu Jiang, Ellen T. McCarthy, Ram Sharma, Madhulika Sharma, Gregory Vanden Heuvel, Virginia J. Savin, Pramod B. Mahajan, and Mukut Sharma
Background: CKD and obesity are marked by elevated pro-inflammatory cytokines, including IL-6. Pregnant obese women are associated with 1.5- to 2-fold increase in serum IL-6, newborns with smaller kidney/body weight ratio, kidney anomalies and increased susceptibility to CKD. Maternal IL-6, but not TNFα or IL-1β, can cross the placental barrier and enter fetal compartment.
Objective: We examined the role of (a) maternal injection of IL-6 during mid-gestation, similar to levels observed in pregnant obese women, on kidney development as a specific molecular surrogate of gestational inflammation and (b) IL-6 on glomerular filtration barrier.
Design/Methods: Pregnant mice received IL-6 (10 pg/g ip) on alternate days from E12.5 to end of gestation while the control pregnant mice received normal saline. Following euthanasia, newborn kidneys were fixed in 10% formalin or OCT, or used to isolate RNA or protein lysate. We used in vitro albumin permeability assay to study the effect of IL-6 on filtration barrier.
Results: Mid-gestational administration of IL-6 (10 pg/g) to pregnant mice resulted in newborns with lower body (p<0.001) and kidney (p<0.001) weights [Figure i]. Histomorphometry showed decreased nephrogenic zone width (p=0.039), increased numbers of mature glomeruli (p=0.002), and pretubular aggregates (p=0.041) [Figure ii]. Immunostaining for podocyte markers showed increased number of mature glomeruli (p<0.001), LC-MS for CpG DNA methylation revealed increased 5mC levels (p<0.05), and Western blotting showed upregulated JAK2/STAT3 (p<0.05) [Figure iii]. RT-qPCR Array analysis of cell-cycle and apoptosis genes also suggested accelerated maturation. In vitro studies using isolated rat glomeruli showed that IL-6 (0.01-5 pg/mL) significantly increased glomerular albumin permeability (p<0.001) which was blocked by pretreatment with anti-IL-6 antibody suggesting its direct effect on the glomerular filtration barrier. IL-6 caused derangement of the actin cytoskeleton and upregulation of pJAK2/pSTAT3 in murine podocytes that maintain the glomerular barrier function.
Conclusion(s): Perinatal exposure to IL-6, a surrogate of maternal inflammation, resulted in small kidneys with accelerated maturation and upregulated JAK-STAT signaling. IL-6 injures the glomerular filtration barrier. We propose to use this animal model to study susceptibility to CKD in adult offspring to determine the long-term effects of the growing incidence of maternal obesity, obesity and CKD across the globe.Presented at the 2021 PAS Virtual Conference
-
Peripartum Antibiotics Induce Dysbiosis and Predispose the Neonatal Gut Towards Inflammation
Alain Cuna, Marianne N. Nsumu, and Venkatesh Sampath
Background: Broad-spectrum antibiotics in preterm infants have been associated with necrotizing enterocolitis (NEC), but the exact mechanisms that explain this association remain poorly defined.
Objective: To examine the impact of peripartum antibiotics on gut microbiota and intestinal inflammation in the developing gut.
Design/Methods: C57BL6 dams were administered broad spectrum antibiotics mixed with sterile drinking water from E15 to postnatal day (P)14 (Fig 1). Gut microbiota were analyzed by targeted 16S PCR for total bacterial density and relative abundance of major bacterial phyla. Effects of antibiotics on inflammatory TLR-signaling and injury in the neonatal gut were evaluated with PCR and histology.
Results: Peripartum antibiotics reduced gut bacterial density (Fig 2A) and diversity (Fig 2B) of treated dams compared to untreated controls. Decreased gut bacterial density was also evident among pups of antibiotic-treated dams starting at P8 and persisting to P21 (Fig 2C). Investigation of TLR signaling by PCR showed that at P8, pups of antibiotic-treated dams have significant upregulation of TLR4 signaling (TLR4, IRAK1) and inflammatory cytokines (KC, ICAM1) in the gut compared to pups of untreated controls (Fig 3A). Increased gut TLR4 inflammatory signaling persisted to P21 despite discontinuation of antibiotics by P14 (Fig 3B). Histologic evaluation of terminal ileum revealed that antibiotics alone were insufficient to elicit intestinal injury consistent with NEC (Fig 4).
Conclusion(s): Antibiotic exposure during the early critical period after birth induces gut dysbiosis and negatively impacts the developing gut towards a pro-inflammatory state. These results support ongoing efforts of antibiotic stewardship to avoid routine antibiotics in preterm infants without risk factors for sepsis. Future experimentation is ongoing to assess the effects of shorter antibiotic duration and addition of noxious stimuli on TLR signaling and other markers of intestinal injury.Presented at the 2021 PAS Virtual Conference
-

Physicians’ Burnout: A First Step to Development of a Wellness Curriculum
Tyler Smith, Katherine E. Mason, David D. Williams, and Kadriye O. Lewis
Background: Prevalence of burnout among physicians is a critical issue impacting all career levels. Identifying burnout begins in medical training with trainees and early career physicians at risk for depression and burnout1. Participation in wellness programs may mitigate burnout perhaps during the COVID-19 pandemic. Online physician wellness activities i.e., coaching and training are offered at a free-standing children’s hospital in the Midwest USA. These programs are well received, but there is no specific curriculum addressing physicians’ wellness needs within the Division of General Academic Pediatrics (GAP). In designing a meaningful program, we conducted a needs assessment survey to gauge GAP physicians’ current involvement in wellness activities and participation challenges.
Objective: To determine a framework and core curriculum leading to the development and implementation of an impactful wellness curriculum for GAP physicians.
Design/Methods: This survey study used a discrepancy-based needs assessment approach to obtain data from GAP physicians at Children’s Mercy Kansas City (CMHK) about their wellness activities. We developed a survey with sections about wellness activities (7 items) and demographic information (6 items). We piloted the survey with 16 academic pediatricians outside the Division to assess the items’ clarity. The survey was put on REDCap and sent to GAP physicians with 6 reminders sent between July-October 2020. Descriptive statistics: frequencies, percentages, means and standard deviations were used to analyze the data. We obtained Institutional Review Board approval from CMHK.
Results: Of 46 GAP physicians surveyed, 24 (52%) completed the survey. Twenty-one (87.5%) physicians participated in weekly wellness activities with 13 (54%) participating more than three times weekly. Barriers to participation included time (96%), clinical duties (91%) and personal responsibilities (81%). GAP physicians preferred wellness activities such as mindful thinking (81%), meditation breaks (70%), microlearning with mobile devices (68%) and mid-day fitness activities (65%).
Conclusion(s): Our study results provided useful information about desired wellness activities and potential barriers that may affect GAP physicians. We plan to use these findings when designing wellness curriculum in the context of instructional design and content selections.Presented at the 2021 PAS Virtual Conference
-

Prenatal diagnosis of an uncommon form of a hypoplastic left heart syndrome variant.
Anmol Goyal, Kelsey Pinnick, Rita France, and Maria Kiaffas
Background: Mitral valve dysplasia syndrome (MVDS) is a rare form of congenital heart disease, similar to hypoplastic left heart syndrome (HLHS). Prenatal identification is important for counseling, delivery planning and postnatal management.
Case: A 39 year-old woman underwent fetal echocardiography at ~34 weeks gestation for evaluation of fetal cardiomegaly and hydrops revealing: biatrial enlargement, mild-to-moderate mitral and tricuspid valve insufficiency, echobright mitral valve apparatus, biventricular dilation, severe LV fibroelastosis (EFE) and systolic dysfunction, mild hypoplasia of aortic valve annulus and aortic arch, and a thick restrictive atrial septum (RAS) with left to right flow (Fig 1a-c).
Decision‐making: Although critical aortic stenosis was considered initially, MVDS seemed more likely given above characteristic findings. Delivery planning included elective C-section with standby catheterization laboratory and ECMO teams, given RAS and cardiac dysfunction. Patient was listed for transplant as biventricular or single ventricle repair were deemed unfeasible, given valvar insufficiency, LV dysfunction and EFE (Fig 1d-g).
Conclusion: MVDS is uncommon but should be considered with HLHS differential, in presence of a normal-dilated left atrium and ventricle, LV dysfunction and EFE, RAS and aortic valve and arch hypoplasia. Planned delivery and immediate postnatal atrial septostomy is warranted and cardiac transplantation is often the only therapeutic option.
-

Prevalence of Mycoplasma genitalium and Macrolide Resistance in Adolescent Females Receiving Care at a Pediatric Hospital
Kayla Barnes, Bishnu Adhikari, Rangaraj Selvarangan, Christopher J. Harrison, and Melissa K. Miller
Background: Mycoplasma genitalium is an established sexually transmitted cause of nongonococcal urethritis in males and macrolide resistance is increasing. The pathogenic role is less well-defined in adolescent females and guidelines recommend M. genitalium testing only be considered in cases of persistent or recurrent cervicitis and pelvic inflammatory disease (PID). We lack understanding of the prevalence and macrolide resistance of M. genitalium in adolescent females.
Objective: To determine the prevalence of M. genitalium and rate of detected macrolide resistance among adolescent females seeking care at a pediatric children’s hospital.
Design/Methods: We collected 200 salvaged urogenital samples (56 urine and 144 vaginal) from adolescent females aged 12-17 years seeking care between November 1, 2019 and April 31, 2020. We used Aptima Mycoplama genitalium assay (Hologic) to detect M. genitalium, Lightmix Modular Mycoplasma Macrolide kit (TIB MOLBIOL) to determine macrolide resistance, and confirmed findings by using Sanger Sequencing. We reviewed electronic medical records to determine presenting symptoms, concurrent urinary tract or sexually transmitted infections, demographics, and sexual risk behaviors. To look for associations with presence of M. genitalium, we used t-tests and chi-square or Fisher’s Exact tests.
Results: The prevalence of M. genitalium was 9.5% (95% CI, 5.4, 13.6). Of the 19 positive specimens, 5 were urine and 14 were vaginal samples. Macrolide resistance was detected in 89.5% positives (95% CI, 75.7, 100). Both susceptible positives were from vaginal specimens. Among these positives, 89.5% had history of positive/negative sexual experience documented and 53% reported history of vaginal intercourse. Compared to those without co-infection, females with any co-infection were more likely to have M. genitalium (6.6% vs. 18.4%, p=0.023). The most common co-infection among positives was Chlamydia trachomatis (26.3%) and nearly all (80%) of these patients received azithromycin. The mean age for females with M. genitalium was somewhat higher than those without (17.1 + 0.7 vs 16.4 + 1.7, p=0.057). Compared to white females, black females were more likely to have M. genitalium (3.3% vs 17.4%, p=0.015%).
Conclusion(s): M. genitalium can often be detected among genitourinary samples from adolescent females and is nearly always resistant to macrolide antibiotics. Further work is needed to clarify the potential pathogenic role of M. genitalium in adolescent female reproductive health.Presented at the 2021 PAS Virtual Conference
-

Rates of Positive Suicide Screens among the Emergency, Inpatient and Outpatient Clinics at a Tertiary Care Children’s Hospital
Fajar Raza, Hung-Wen Yeh, John Lantos, Mark Connelly, and Shayla Sullivant
Background: Prior research has suggested that rates and acuity of suicidality are elevated among patients seen in EDs and in certain clinics. However, the occurrence and severity of suicide risk has been rarely studied in the pediatric clinic populations due in part to unsystematic screening. We examined suicidality across different pediatric clinical care settings based on data from our newly implemented hospital-wide suicide risk screening program.
Objective: To determine a) which patient populations presented with the highest rates of suicidality; and b) the percentage of patients who had current thoughts of suicide and were thus deemed “acute.”
Design/Methods: We conducted a retrospective analysis of the clinical data repository. Adolescents were screened for suicide risk between Feb 2019 and Jan 2020. Patients were eligible for suicide risk screening if they were >12 years old and had a medical visit in the inpatient (IP), emergency (ED), urgent care (UC), or outpatient (OP) clinics of a dedicated pediatric hospital in the midwest. We used the 4-question ASQ (Ask Suicide-Screening Questions) by which a positive response to any of the 4 questions was considered a positive screen. Among positives, those who gave a positive response to question 5 (“are you having thoughts of killing yourself right now?”) were classified as “acute risk.”
Results: Out of the 101,732 screenings completed during this time, 11,460 (11.3%) were positive, and 734 were at acute suicide risk. Overall positivity rates were highest among inpatients (18.6%), followed by the ED (18.0%), OP clinics (9.5%), and UC (8.8%). The highest rate of acute positives was found in the ED (3.1%), followed by IP (2.0%). The lowest rates of acute risk were observed for UC (0.2%) and OP clinics (0.1%). Among UC clinics, the highest rates of suicidality occurred in the Child Abuse Clinic (40.2%), followed by Adolescent Medicine (24.9%), Sleep and Teen Clinics (both 17.6%). The highest rate of acute suicide risk occurred in the Child Abuse Clinic (1.7%).
Conclusion(s): Suicidality among pediatric patients is highest among adolescents seen in the inpatient unit and those seen in the ED. Some pediatric outpatient clinics also have high rates of suicidality but the rate of acuity appears to be lower in this setting relative to the inpatient and ED setting. Data on the acuity of risk and on the prevalence of acute risk in different clinical settings can be used to plan for allocation of mental health resources to follow-up on positive screens.Presented at the 2021 PAS Virtual Conference
-

Recurrent neonatal herpes simplex virus infection associated with IRF7 and UNC93B1 variants
Venkatesh Sampath, Megan H. Tucker, Heather Menden, Sheng Xia, Wei Yu, and Nikita Raje
Background: Neonatal herpes simplex virus (HSV) is a devastating disease with high mortality. In adults and children, genetic variants in the toll-like receptor 3 (TLR3) pathway increase susceptibility to herpes simplex encephalitis (HSE), but the genetic basis of susceptibility to neonatal HSV is unknown. We hypothesized that deleterious variants in the TLR3 pathway increased vulnerability to HSE in neonates. We investigated immunogenetic studies in an infant with neonatal skin, eye, mouth (SEM) HSV followed by HSE.
Objective: To combine exome sequencing with in vivo and in vitro immune functional analysis to discover the immunogenetic basis of HSV vulnerability in proband.
Design/Methods: The proband developed SEM HSV1 on day 7 of life and recovered fully with acyclovir. At 1 year of age he presented with seizures and was diagnosed with HSV1 HSE. Exome sequencing was performed to identify pathogenic genetic variants. An immune work up including peripheral blood monocyte (PBMC) functional TLR assay was done. Wild type and mutated alleles were transfected into THP1 monocyte cell line stably expressing an interferon regulatory factor 3 (IRF3) promoter-driven luciferase reporter. Poly(I:C) (1ug/mL), a TLR3 ligand, was used to stimulate THP1 for 24hr prior to luciferase assay and qRT-PCR for interferon (IFN) α and β gene expression.
Results: We identified rare missense mutations in interferon regulatory factor 7 (IRF7) (p.Arg100Pro) and UNC-93 Homolog B1 (UNC93B1) (p.Pro404Ser) genes. Immune work up including CD4, CD8, NK cell, and immunoglobulins was normal, except for a total loss of PBMC cytokine response to TLR3 stimulation (Fig.1). Luciferase assays in THP1 showed dramatically reduced TLR3-driven IRF3 promoter activity in response to poly(I:C) with IRF7 and UNC93B1 variants (Fig. 2 & 3). Similarly, IFNα and IFNβ expression induced by poly(I:C) was enhanced by wild type IRF7 and UNC93B1 alleles, but strongly suppressed by mutant IRF7 and UNC93B1 alleles (Fig. 2 & 3). Combining the 2 mutant alleles compounded disruption of TLR3 signaling (Fig. 4).
Conclusion(s): We identified 2 variants (IRF7, UNC93B1) that disrupted the TLR3-response to HSV in vitro and in vivo in an infant with recurrent HSV. This is the first report of human HSV disease associated with IRF7 mutation. Neonatal HSV may be a phenotype for immunodeficiency in the TLR3 pathway genes. Infants with severe neonatal HSV may warrant genetic screening to identify variants that increase recurrence risk, and prolonged acyclovir prophylaxis should be considered.Presented at the 2021 PAS Virtual Conference
-

Registration of newly diagnosed children with autism spectrum disorder and developmental disabilities at state regional offices
Whitney Rolling and Rachel Goodson
• In fiscal year 2020, 39,220 Missouri residents utilized developmental disability services through the Missouri Department of Mental Health.1 • Developmental disability services account for 53% of Missouri’s state mental health funding (about 1.3 billion dollars annually).
• Physicians and psychologists are required for making eligible diagnoses, but registration for state support is patient dependent and can be perceived as an extensive paperwork process.
• Project Goal: Measure and increase the percentage of eligible patients registered for their state mental health resource offices.
-

Response to dexamethasone predicts diagnosis of severe (type 2) bronchopulmonary dysplasia or death
Christopher R. Nitkin, Keith Feldman, Alain Cuna, Alexandra Oschman, William E. Truog, Michael Norberg, Jane Taylor, and Tamorah Lewis
Background: Bronchopulmonary dysplasia (BPD) is the most common respiratory morbidity after preterm birth but requires diagnosis at 36 weeks postmenstrual age (PMA). Dexamethasone is often used to treat infants at high-risk of BPD. The ability for earlier prediction of BPD, based on steroid response, could be useful as a surrogate marker for new therapies.
Objective: To construct a model that predicts severe BPD or death at 36 weeks PMA based on clinical response to dexamethasone.
Design/Methods: Retrospective chart review of preterm infants treated with dexamethasone between 2010-2020 at a Level IV NICU with data collected on demographics, age of steroid initiation, mode and level of ventilatory support during treatment, and pCO2 on day 1, 3, and 7 of steroid use. Highest mode of ventilation was assessed as either high frequency oscillatory ventilation, conventional invasive ventilation, or any form of non-invasive ventilatory support; while support level was represented by respiratory severity score (RSS = MAP*FiO2). BPD outcomes were defined according to the 2017 BPD Collaborative definition. The composite of mild, moderate, or severe (type 1) BPD was used as referent group to assess odds against the composite of severe (type 2) BPD or death.
A regularized logistic model was fitted using the following variables: gestational age, sex, age of steroid initiation, baseline (Day 1) and percent change from baseline (Day 7 vs Day 1) in RSS and pCO2, and ventilator mode change from baseline. The resulting predicted probabilities were divided into quartiles to obtain a discrete risk level (level 1 to 4).
Results: 94 infants were treated with dexamethasone prior to 36-week BPD assessment. A 10,000-iteration bootstrap was performed, and a risk score was predicted for infants not included in the resampled data at each iteration. The proportion of those with severe (type 2) BPD or death at each risk level were evaluated (Figure). For comparison, predictions were also made with a baseline model using only demographic data. Increasing risk category was well aligned with rising outcome incidence, increasing from ~20% of infants at level 1 to just over 55% of infants at level 4.
Conclusion(s): The addition of changes in ventilatory parameters with dexamethasone improved BPD prediction compared to baseline demographics alone. Incorporating drug response phenotype into a BPD model may enable more rapid development of future therapeutics.Presented at the 2021 PAS Virtual Conference
-

Simulation Based Clinical Systems Testing in the Pediatric Emergency Department to Prepare for COVID-19 Pandemic
Christopher S. Kennedy, Marc Sycip, Lisa Ell, and Shautonja Woods
Background: The COVID-19 prompted pediatric emergency departments (PED) to prepare for a surge in patients. In response, guidelines developed represent “work as imagined” and may not reflect work as done. In situ simulations could identify gaps and help to mitigate errors. Simulation-based clinical systems tests (SbCSTs) can detect latent safety threats (LSTs) in systems design.
Objective: Our aim was to use SbCSTs combined with rapid cycle training to test hospital system modifications for ED preparation. This method represenst a new application of SbCSTs. The research questions were in 2 frames: 1. Can rapidly deployed SbCSTs identify LSTs and recommendations for improvement and 2. Do providers consider rapid SbCSTs a way to improve preparedness?
Design/Methods: The study took place in a PED and was approved by the IRB as non-human subject research. SbCST scenarios tested guidelines/job aids, equipment, and ways to mitigate exposure. Each case used “tipping-point”(s) to test workflow. Short scripted debriefs reviewed guidelines, staff input, and the simulation repeated. Participants evaluated the SbCST with a survey. Three sim staff collected observations on a standardized form for which process was tested, staff response, and LSTs identified.
Results: Question 1. LST identification: From the 44 simulations, 64 staff identified 103 unique LSTs. LSTs were categorized as follows: Job Aids/tasks 37 (36%), Isolation Measures (PPE) 30 (29%), Communication/personnel: 18 (17.5%), and Equipment 18 (17.5%). Common LSTs identified: In the Job Aid category: simplify intubation job aid, Isolation Measures: staff had concerns about PPE changes prior to generating aerosol, Equipment: adjust equipment needs to avoid delays, and change PPE, and Communication/Personnel: minimizing staff during resuscitations. Question 2. Staff evaluations (strongly agree, (SA) to strongly disagree, (SD)): Worth the time it took: 86% SA, 14% some what agreed (SWA). An acceptable way to improve: 92 % SA, 8% SWA. An effective way to test: 92% SA, 8% SWA. Debriefing allowed staff to share ideas: 86% SA SWA 8%, and Average 6%.
Conclusion(s): This study showed that SbCST methods are adaptable for preparedness evaluation and training. Participant evaluations reveal a high regard for this method for practicing/improving the COVID-19 process. This work highlights a new application of SbCSTs that could increase system preparedness and reduce errors.Presented at the 2021 PAS Virtual Conference
-

Simulation Based Clinical Systems Testing of a Pediatric ED to Improve Staff and Process Readiness for Pediatric Hypoglycemia
Kevin Meilak MD and Christopher S. Kennedy
Background: Hypoglycemia is the most common metabolic disorder in children in pediatric emergency department (ED) settings 1. Children may present with nonspecific symptoms, or asymptomatically2. So identification/treatment is very challenging. Delayed recognition and under treatment can lead to poor patient outcomes including seizure, coma, and death. Simulation-based clinical systems tests (SbCSTs) are useful to detect gaps/latent safety threats (LSTs) in system design.3-5
Objective: Our aim was to use SbCSTs combined with rapid cycle training to test system function for ED treatment of hypoglycemia.3-5. The research questions were in 2 frames: 1. Can SbCSTs identify gaps/LSTs and recommendations for improvement and 2. Would providers consider SbCSTs acceptable way to improve?
Design/Methods: The study took place in a children’s hospital ED and was approved by the IRB as non-human subject research. We conducted SbCSTs with staff responding to a 5-month old with hypoglycemia and used “tipping-point”(s) in care to emulate challenges and a Gamaurd mannequin and a tablet-based “monitor”(SimMon). Short scripted debriefs reviewed guidelines, staff input, and then staff repeated the simulation. Participants used a survey to evaluate the SbCSTs. Two sim staff observed, and took notes on a standardized reporting form and included staff response, any gaps/LSTs identified.
Results: Preliminary results: 12 SbCSTs were conducted with 22 staff, 13 (59%)(7- MDs, 4-RNs, 2-APRN) filled out anevaluation. For question 1 LST identification: Staff identified 50 LSTs. Each LST was categorized for cause as follows:14 (28%) glucose gel location/administration concern, 12 (24%) need for a better job aid, 10 (20%) were related to dextrose dosing errors, 7 (14%) POC glucose recheck timing, and 7 (14%) inappropriate treatment. For question 2: An acceptable process: (strongly disagree, SD to strongly agree, SA): Worth the time it took: 85% SA, 15% somewhat agreed (SWA). Improved staff readiness: 85 % SA, 15% SWA. An effective way to test/provide solutions: 85% SA,15% SWA. The debrief allowed staff to share ideas: 85% SA, 15% SWA.
Conclusion(s): This study demonstrated that simulation-based clinical systems testing (SbCST) methods are adaptable for use in a children’s hospital ED for preparedness evaluation and training. Participant evaluations demonstrate a high regard for this method. The process detected many LSTs but further data analysis with a formal FMEA process will be performed. -

Spanish-speaking families’ perspectives on the acceptability and impact of culture and language coaching for bilingual residents
Ryan Northup, Francisco Martinez, and Jeffrey D. Colvin
Background: Culture and language coaching in the CHiCoS (Clínica Hispana de Cuidados de Salud) Program provides bilingual (English-Spanish) residents with longitudinal, personalized training in health care Spanish and cultural aspects of care. This intensive 1:1 training by a culture and language coach (CLC) over three years has been shown to improve residents’ skills and family satisfaction with care. Families’ perspectives on acceptability of the presence and impact of the CLC during visits have not been formally described.
Objective:
Design/Methods: In this descriptive, cross-sectional pilot study, we surveyed Spanish-speaking caregivers who received care from any of 18 bilingual CHiCoS residents accompanied by a CLC in our academic pediatric primary care clinic. The 10-question survey was created by the study team in Spanish using a formal process including piloting and revision. Respondents surveyed by telephone after their visit were asked how well the resident spoke and understood Spanish, effectiveness of communication, how the CLC impacted communication, future preference for coached vs interpreted visits, and overall satisfaction.
Results: Sixty of 67 recruited parents (90%) completed the survey. A majority reported that their resident spoke (65%) and understood (63%) Spanish very well, with little or no intervention needed from the CLC. The remainder felt that the resident spoke well but needed occasional support from the CLC to achieve complete communication. None had major difficulty understanding their resident. Overall communication was either “very easy and direct without problems” (57%) or “more or less easy,” with problems being “quickly resolved” (43%). Most felt that the CLC improved communication “a lot” (77%) or “somewhat” (10%). For a hypothetical future visit, 58% preferred a coached visit with a doctor speaking at least some Spanish to an interpreted visit with a doctor speaking no Spanish; the remainder said either option would be equally good. None preferred an interpreted visit. All respondents were either “very satisfied” (83%) or “satisfied” (17%) with the care given by the resident-CLC team.
Conclusion(s): Spanish-speaking caregivers strongly support culture and language coaching for bilingual pediatric residents and described positive impact on in-visit communication. Despite the majority of CHiCoS residents not yet passing their validated language proficiency exams, all families reported complete communication and satisfaction with their visits.Presented at the 2021 PAS Virtual Conference
-

Teaching Pediatric Procedural Pain and Anxiety Management to Residents: Early Outcomes of a Newly Developed Curriculum
Jennifer J. Dilts, Brian R. Lee, Shobhit Jain, Ross Newman, Sarah Fouquet, Michael Brancato, and Kadriye O. Lewis
Background: Poorly managed pediatric pain has negative long-term outcomes, including needle phobia, increased pain and anxiety with subsequent procedures, and healthcare avoidance in adulthood. Evidence-based interventions to reduce procedural pain and anxiety are vastly underutilized, and a literature search revealed no specific curriculum to teach residents optimal skills for pain and anxiety management in minor procedures (e.g. venipuncture, laceration repair). Thus, we developed a multimedia-based lecture with PowerPoint, utilizing results from a focus group interview (conducted with 7 pediatric residents, to determine educational content and identify residents’ needs and learning preferences).
Objective: To measure residents’ learning outcomes (knowledge, attitudes, perceived competence, and practice change) and satisfaction with a newly developed procedural pain and anxiety curriculum.
Design/Methods: Pediatric and combined internal medicine/pediatric residents were invited to complete the curriculum online through the in-house learning management system (Cornerstone) during their emergency medicine rotation. Data were collected between July 2019 and June 2020 (pre- and post-tests, as well as a follow-up survey 3-12 months later). McNemar’s test was used to measure pre- and post-test knowledge gains while Wilcoxon signed-rank test was used to compare changes in attitudes, perceived competence, and reported changes in procedural management.
Results: Seventy-two residents were invited to participate, with 28 completing the intervention with pre- and post-tests (39% completion rate) and 12 of those residents completing the follow-up survey. Residents increased their knowledge by 24.3% (p<0.0001) (Figure 1). There was no significant change in attitudes towards pain and anxiety management. Positive improvements, although non-significant, were seen in perceived competence and reported change in medical practice (Figures 2 and 3). Course evaluation data found that 75% of residents planned to utilize knowledge from the course in the next few weeks (Table). The majority of residents who completed the follow-up survey reported that knowledge learned in the course improved their practice and/or led to changes in their practice.
Conclusion(s): Early outcomes of the curriculum revealed significant knowledge increase. Additionally, these results provide a foundation for evaluation of an online game-based version of the curriculum, which we plan to make available to learners beyond our home institution.Presented at the 2021 PAS Virtual Conference
-

Using Standardized Scripting to Improve Antibiotic Stewardship in a National Pediatric Urgent Care Collaborative
Amanda Nedved, Melody Fung, Cindy Liu, Rana Hamdy, and Amanda Montalbano
Background: A study using administrative data reported urgent care providers as having the highest rates of inappropriate antibiotic use for upper respiratory illnesses. In a national survey, pediatric urgent care providers reported family expectations as a primary driver for prescribing inappropriate antibiotics. Standardized scripting has been effective at reducing unnecessary antibiotics while increasing family satisfaction.
Objective: To reduce inappropriate prescribing for upper respiratory infections (acute otitis media (AOM), otitis media with effusion (OME), and pharyngitis) in pediatric urgent cares by 20% by December 1, 2020 through use of standardized scripting in Year 2 of a national pediatric urgent care quality improvement collaborative.
Design/Methods: Participants were recruited via email, newsletters, and webinars from pediatric urgent care national societies. Each site committed at least 3 providers who each submitted data from 10 encounters per month. Antibiotic prescribing was defined as appropriate based on consensus guidelines. Previously published antibiotic stewardship scripting for viral upper respiratory infections was adapted for use with the three target diagnoses. Patient and family advisors reviewed all scripting and their feedback was incorporated into the revised standardized scripting. Clinical examples for each diagnosis using the standardized scripting were provided to the collaborative by use of digital cartoon videos, written framework, and templated discharge instructions. Data from clinical encounters were submitted via a REDCap form, analyzed for inappropriateness, and reported back to participating sites via run charts during monthly webinars.
Results: The 104 participants from 10 institutions submitted 1,150 encounters for analysis in the intervention cycles (May-December 2020). Overall inappropriate antibiotics decreased from 26.4% to 16.6% (p=0.13). Inappropriate antibiotic use decreased in AOM (38.6% to 26.5%; p=0.12) and pharyngitis (14.5% to 8.8%; p=0.26). OME increased from 30.8% to 46.7% (p=0.18) (Figure 1). During the study immediate antibiotic prescriptions for OME decreased; however, delayed prescribing increased (Figure 2).
Conclusion(s): In its second year, this national collaborative developed standardized scripting to overcome the barrier of perceived family expectations to decreases inappropriate antibiotic prescriptions in pediatric urgent care for AOM and pharyngitis. Future interventions will target the inappropriate use of delayed prescribing in OME.Presented at the 2021 PAS Virtual Conference
-

Utilization of Enteral Tranexamic Acid To Stabilize Gastrointestinal Hemorrhage in Pediatric Patients on ECMO
Gina Patel, Jenna Miller, Thomas M. Attard, and Asdis Finnsdottir Wagner
Hemorrhagic and thrombotic complications on Extracorporeal Membrane Oxygenation (ECMO) support are associated with significant morbidity and mortality. There is a paucity of literature describing the incidence and management of Gastrointestinal (GI) bleeding on ECMO. We describe the use of enteral tranexamic acid (TXA) as an alternative strategy in two pediatric patients with GI hemorrhage on ECMO. Case 1 A 5-year-old with Wilms Tumor required Veno-Venous ECMO due to respiratory failure associated with pulmonary hemorrhage and air-leak syndrome. Her course was complicated by severe GI hemorrhage refractory to IV proton pump inhibitor (PPI), IV TXA and octreotide infusions. Concomitant IV TXA and cessation of systemic anticoagulation coincided with emergent transition to Veno-Arterial (VA) ECMO after cannula thrombosis. Procedural interventions included esophagogastroduodenoscopies (EGD) revealing gastric ulcers, two endovascular embolization procedures, and a third arteriogram due to continued bleeding that did not identify a source. Enteral TXA (20 mg/kg q 8 hours) was then begun with resolution of GI bleeding, reduction in blood product transfusion and no further emergency circuit changes. She survived to hospital discharge. Case 2 A 3-year-old with a burn injury required VA ECMO due to cardiopulmonary collapse. Her course was complicated by GI hemorrhage. She received a PPI, octreotide infusion and was started on IV and enteral TXA (10 mg/kg q 8 hours). An EGD did not identify a bleeding source. There was no interruption in circuit anticoagulation or integrity. She remained on enteral TXA for 48 hours until GI bleeding resolved. She survived to ECMO decannulation. Patients supported by ECMO require systemic anticoagulation thus making GI bleeding difficult to manage. We report the use of enteral TXA to provide anti-fibrinolysis. This was associated with cessation of bleeding but not associated with further circuit thrombosis. Enteral TXA can be an additional tool used for GI bleeding on ECMO.
-

Virtual Child Neurology Education During COVID-19 and Beyond
Jennifer J. Dilts and Rose N. Gelineau-Morel
Background: Even prior to the Coronavirus Disease 2019 (COVID-19) pandemic, Children’s Mercy Kansas City’s large neurology division struggled to engage learners in educational conferences. With 113 division members across 5 locations, attending conferences was challenging. While some conferences were live-streamed, we offered no recorded lectures, and most conferences were attended solely by trainees and 3-4 select faculty. COVID-19 eliminated in-person group learning opportunities.
Objective: We aimed to rapidly develop and implement a comprehensive and inclusive virtual child neurology curriculum and assess its impact.
Design/Methods: We created a neurology education “team” using Microsoft® Teams. Within 1 week of beginning social distancing, we offered an average of 4 live virtual lectures per week, increased from 2 weekly lectures prior to COVID-19. Lectures covered diverse topics (e.g. quality improvement, empathy, leadership) in addition to clinical neurology. We recorded and stored all lectures and supplementary materials in Microsoft® Teams. We distributed a survey after the third and fourth weeks of virtual education, and again after 3 months.
Results: Survey response rate was 92% (104/113) for week 3, 84% (95/113) for week 4, and 55% (62/113) at 3 months. Percentage of learners attending at least 1 lecture per week increased from 28% (pre-COVID-19) to 74% (week 3), and this gain was sustained at 3 months (88%) (Figure 1). Attendance was well-distributed amongst all types of learners (Figure 2), averaging 22 participants per lecture (SD 9.2). Mean learner satisfaction increased from 5.7 out of 10 (pre-COVID-19, SD 2.3) to 8.5 out of 10 (3 months, SD 1.25, 2-tailed paired t-test p<0.001) (Figure 3). Learners appreciated easy access to educational materials, including viewing recorded lectures. At 3 months, 88% of respondents wished to continue virtual education, and 60% of clinical staff planned to change their work practice based on information they learned. Sixty-seven percent of trainees “agreed” or “strongly agreed” that the virtual curriculum improved how prepared they felt for upcoming examinations. Rapport across the division increased, with 85% of respondents feeling more connected to colleagues.
Conclusion(s): COVID-19 was a disruptive innovation, catalyzing the rapid formation of a virtual neurology curriculum. Our curriculum increased learner satisfaction, engagement, and rapport. Nine months into the pandemic, we continue to offer several virtual neurology lectures each week.Presented at the 2021 PAS Virtual Conference
-

Where are they now? Spanish utilization and career direction of graduates of a pediatric bilingual continuity clinic
Jodi Dickmeyer, Katie McAnany, Sarah Stone, and John Cowden
Background: The Clínica Hispana de Cuidados de Salud (CHiCoS) Program was created in 2009 to prepare bilingual (English-Spanish) pediatric residents to independently give safe, effective care to Spanish-speaking families. By providing 1:1 support from a culture and language coach over three years of residency, CHiCoS has improved residents’ cultural and linguistic skills and families' perceptions of care. The effects of such training on residents’ future careers have not been formally studied.
Objective: To describe the careers of former CHiCoS residents, the impact of culture and language training on their practice, and opportunities for post-CHiCoS cultural and language training.
Design/Methods: In this descriptive, cross-sectional study, we created and sent a digital survey (26-44 questions depending on branching logic) to former CHiCoS residents including details of their current and previous practice, Spanish utilization with patients/families, maintenance of Spanish proficiency, impact of CHiCoS on career satisfaction, and desire for ongoing culture and language training. All CHiCoS residents graduating from 2011-2019 were included, except those who did not complete the program or who were authors of this study.
Results: Twenty-four of 33 CHiCoS graduates (73%) completed the survey. A majority worked in academic (14/24) and urban (14/24) settings. Almost all who were qualified bilingual staff upon CHiCoS graduation (N=18) worked in settings with Spanish-speaking patients/families (94%) and used their Spanish skills in greater than half of their visits (89%). Among graduates seeing >20% Spanish speaking patients (N=9), all but one felt they maintained or improved their Spanish skills. Most of those with <20% Spanish-speaking patients (10/13) reported maintaining their proficiency level, while those with no Spanish-speaking patients (N=2) felt their skills had eroded. CHiCoS training had a moderate to large impact on career satisfaction for 83% of graduates (Table, Figure), and 71% reported a desire for further support in cultural and linguistic skill development, including post-CHiCoS culture and language coaching.
Conclusion(s): Culture and language coaching for bilingual residents leads to careers serving culturally and linguistically diverse patients and families. Language skills developed in residency can be maintained through ongoing use in future practice, but most graduates would like to continue formal culture and language training, even after reaching a professional level of proficiency.Presented at the 2021 PAS Virtual Conference
-
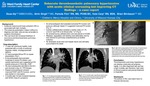
Subacute thromboembolic pulmonary hypertension with acute clinical worsening but improving CT findings - a case reporrt
Doaa Aly, Alvin Singh, Pamela Finn, Kate Carp, and Brian Birnbaum
ackground: • Subacute massive pulmonary embolism (PE) is associated with high mortality. • The subacute presentation makes it difficult to diagnose and older clots are less amenable to systemic thrombolysis. • This can result into increased likelihood of recurrence and thromboembolic pulmonary hypertension Case description: • 17-year-old, previously healthy male presented with a month of exertional dyspnea, initially misdiagnosed with asthma. • CT demonstrated diffuse PE on repeat presentation (Fig1). • Echocardiography demonstrated moderate to severe RV dilation and systolic dysfunction and suggested an RV systolic pressure of 73mmHg + RAP. • He was subsequently admitted to the ICU and received a day of r-TPA therapy. • Repeat echocardiogram showed improved RVSP and RV function, and he was started on rivaroxaban. • 3 months later he had increased dyspnea with NYHA Class III symptoms • An echocardiogram demonstrated worsened RV function and pressure, although repeat CT suggested improved PE burden (Fig. 2). • Cardiac catheterization revealed a cardiac index of 1.75 L/min/m2 and PVR of 23 Wood Units * m2 (Fig 3). • He arrested during catheterization and was placed on ECMO. • Alteplase, angioplasty and stenting were attempted, and he was referred for pulmonary endarterectomy at another institution. • He developed acute renal and hepatic failure and ultimately succumbed to his death. Conclusion: Thromboembolic pulmonary hypertension can develop subacutely yet progress rapidly. It is often diagnosed late and has a high mortality rate; therefore, high index of clinical suspicion and prompt treatment is imperative. Disclosure: The authors of this case report have no financial disclosures. Fig 1: CT at initial presentation demonstrating widespread PE with multiple filling defects seen throughout the segmental pulmonary arteries to all lobes of both lungs Fig 2: CT 3 months later, significant obstruction of the distal pulmonary vasculature bilaterally and pruning, giving a false impression of improved clot burden Fig 3: (a) Cath angiography on the first day of readmission (3 month post initial presentation, showing significant obstruction of the right lobar arteries and severely attenuated peripheral pulmonary vasculature. (b) cath angiography on the following day showing rapid progression with almost absent peripheral vascular flow.
-

“ECMO IN A BAG”: Successful Adaptation and Implementation of a Novel Conference Idea
Johanna I. Orrick, Debra E. Newton, Kari L. Davidson, Jenna Miller, and Alyssa Stoner
INTRODUCTION: Extracorporeal Membrane Oxygenation (ECMO) is an ever-evolving technical landscape that requires an advanced level of education. At our institution, a 367-bed pediatric teaching and research facility, learners include registered nurses, registered respiratory therapists, advanced practice registered nurses, resident physicians, pediatric and neonatal intensive care physicians. A certification class followed by an advanced course covers ECMO diagnoses, complications, equipment, and management prior to providing care for ECMO patients in our institution. Educational strategies include high and low fidelity simulations, didactic learning, and clinical hours at the bedside. A desire to increase the experiential learning opportunities was identified as an ECMO leadership goal. In 2018, a team member attended a conference and returned with a low fidelity simulation concept “ECMO in a Bag” from The Hospital for Sick Children in Toronto, Canada. This novel educational concept was subsequently adapted into a dynamic experiential teaching tool that met the interactive learning needs of the Children’s Mercy ECMO educational curriculum. METHODS: The “ECMO in a Bag” concept was first observed in May 2018 at the International Pediatric Simulation Society Workshop. The first version for our hospital was established with laminated equipment photographs and labels in September 2018 and was expanded upon in November 2018 to include non-sterile tubing to connect the photographs together schematically. The tubing, photos, and labels were intended to be used as an assessment for early ECMO learners. Introduction of “ECMO in a Bag” occurred in the August 2019 ECMO certification course. Modifications were implemented to develop an “Introductory ECMO in a Bag” after observations of the novice course participants deemed the task too difficult. In February 2020, the Advanced ECMO course utilized “ECMO in a Bag” in its original version for advanced learners. The class was divided into two teams and then competed against each other to correctly “assemble” an ECMO pump. All participants completed post surveys for each educational experience. RESULTS: When the original “ECMO in a Bag” was applied to 10 novice ECMO learners in August 2019 it was regarded as too difficult by the coordinators. The strategy was modified in the moment, using the laminated equipment names matched to an already assembled nonsterile ECMO pump along with definitions. The revised “Introductory ECMO in a Bag” has since been repeated in the ECMO certification course of 15 learners in August 2020. One hundred percent of the novice learners in both the 2019 and 2020 introductory class surveyed stated the hands-on sessions including “ECMO in a Bag” were effective and engaging. Quotes from the post class surveys included “I really enjoyed the breakout session looking at the circuit. Great to start understanding all of the circuit components,” “Hands on visualization was great, allowed for putting information together”. Additional positive feedback was gleaned from the application of the original “ECMO in a Bag” during the Advanced ECMO courses. One hundred percent of the transitional learners surveyed scored the hands-on portion of ECMO learning as beneficial. Comments included “Enjoy breaking up the talks with hands on activities,” and “I enjoy the games! It really breaks up the day.” DISCUSSION: The evolution of the experiential concept of “ECMO in a Bag” has been well received and is ongoing. It has been adapted for two different levels of ECMO learners in our hospital.. It is now used with resident physicians as well during shadowing experiences with the ECMO team. ECMO coordinators also use “ECMO in a Bag” to teach new critical care bedside nurse
-
A unique cause of elbow pain and loss of range of motion in a 13-year-old
Thomas Munro and Brian S. Harvey
A 13-year-old right hand dominant young lady presented to a pediatric sports medicine clinic for evaluation of decreased ROM and pain in her left elbow with an associated locking sensation that had been occurring for over a year. Two weeks prior to presentation, these symptoms had been acutely worsening as she was practicing for over 10 hours per day for an upcoming dance competition. The patient’s pain is described as a “tightness” and is localized to her antecubital fossa medial to her biceps tendon. The feeling of tightness occurs most prominently with end extension and flexion of the elbow. She has had no associated fever, chills, fatigue, weight loss, swelling, bruising, numbness, tingling, previous reported injury in her elbow, or other pain or mechanical symptoms in any other joint. On exam the patient lacked 5-10° of full extension of the elbow on the left while exhibiting 5° of hyperextension on the right. She is tender to palpation (TTP) over the proximal ulna, flexor tendon mass, capitellum, and biceps tendon as it crosses the antecubital fossa. She is not TTP over the medial epicondyle, lateral epicondyle, olecranon, distal ulna, or on any region of the radius. Initial differential remained broad and included biceps tendinopathy, osteochondritis dissecans, subluxation, dislocation, occult fracture, osteochondroma, osteoarthritis, inflammatory arthritis, and heterotrophic ossification, among other possible etiologies. Frontal, oblique and lateral views of the left elbow showed multiple small heterogeneous calcifications in the antecubital space (the largest measuring approximately 1 cm in greatest diameter). No joint effusion, fracture, or dislocation were present. Soft tissue calcifications are caused by a wide range of pathologies, which can be grouped broadly into dystrophic, iatrogenic, metabolic, connective tissue disease, metastatic, and idiopathic causes. To further elucidate these calcifications an MRI with and without contrast of the left elbow was obtained. The MRI showed a Venous Malformation (VM) with associated phleboliths located anterior to the distal humeral diaphysis, in the region of the posterior aspect of the brachialis muscle, with an associated small intraosseous component in the humerus. VMs are present at birth and grow proportionately as the child develops. They are typically cutaneous, subcutaneous, or mucosal but can be located anywhere throughout the body. VM symptom presentation is highly variable and will often become symptomatic later in life. Treatment is controversial and options include symptomatic support (compression or NSAIDS), surgery, sclerotherapy, and possibly targeted therapy with sirolimus. In this instance the patient was referred to orthopedic surgery and vascular malformation clinic for further management. This case showed Venous Malformation to be a rare cause of elbow pain with associated decreased ROM and a locking sensation in a 13-year-old female patient.
-

Development and Interim Analysis of a Cystic Fibrosis-Specific Antibiogram
Claire Elson, Ellen Meier, Douglas Swanson, Rangaraj Selvarangan, Megan Gripka, and Christopher M. Oermann
Antimicrobial therapy is essential to treat cystic fibrosis (CF) lung infections. Empiric antimicrobial selection is generally based on previous culture information and, if available, an institution-specific antibiogram (ABGM). Most institutions antibiograms exclude cultures from individuals with cystic fibrosis, imposing challenges with empiric antimicrobial selection and monitoring susceptibility patterns over time. A cystic fibrosis-specific antibiogram may help drive population-specific antimicrobial selection and improve antimicrobial stewardship.
-

Development of Drive-Through and Mail-In Systems for Obtaining Surveillance Respiratory Specimens in a Pediatric Cystic Fibrosis Center
Ellen Meier, Paula Capel, and Christopher M. Oermann
Routine surveillance cultures are an essential part of health maintenance for people with cystic fibrosis (CF). The Cystic Fibrosis Foundations (CFF) recommends that respiratory cultures be obtained every three months. The CF Care Center at Children’s Mercy Kansas City (CMKC) also obtains respiratory cultures when there is an acute change in respiratory symptoms. The COVID-29 pandemic resulted in ambulatory clinic closures and an inability to obtain surveillance respiratory cultures. A creative solution for obtaining respiratory cultures was needed during the pandemic.



